A Simple Guide to VPAT Certification and Digital Accessibility
The Voluntary Product Accessibility Template (VPAT) provides quality digital literacy in the educational ecosphere. According to reports, organizations without accessible website interfaces lose $6.9 billion annually. Accessibility is a game-changer in delivering individuals seamless experiences while navigating online interfaces.
Today, many educators are interested in curating an inclusive learning experience for learners with disabilities. By doing so, they can attract diverse learners and adhere to Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.0 compliance.
Choosing the proper accessibility solutions in a marketplace flooded with options will play an essential role in this transition. This is where the Voluntary Product Accessibility Template (VPAT) can be a valuable tool in helping educators make data-driven decisions.
This blog decodes VPAT accessibility solutions, their significance, and how educators can harness this tool.
Table of Contents:
- What is VPAT Accessibility?
- VPAT Certification: What is it?
- Why VPAT Accessibility Matters in Education?
- Why Should You Consider Being VPAT Certified?
- How to Get VPAT Certified?
- Decoding VPAT Data
- Step-by-Step Guide to Achieving VPAT Accessibility
- Familiarize Yourself with Accessibility Standards
- Conduct a Thorough Accessibility Audit
- Structure Your VPAT Report for Clarity
- Make Your Text and Visual Content Accessible
- Design Accessible Interactive Elements
- Prioritize Accessible Fonts and Color Contrasts
- Keep VPAT Documentation Updated
- Optimize Content for Multiple Devices
- Train Your Team on Accessibility Standards
- Importance of VPAT in Improving Digital Literacy for Students
- Enhanced User Experience Through Assistive Features
- Encouraging Inclusivity for All Learning Styles and Abilities
- Encouraging Digital Literacy Skills
- Reducing the Digital Divide
- Supporting Legal and Institutional Compliance
- Facilitating Academic and Social Inclusion
- Empowering Educators with Accessible Teaching Tools
- Supports Lifelong Learning Skills
- How Can Educators Harness VPAT Accessibility?
- Wrapping Up
What is VPAT Accessibility?
VPAT accessibility refers to the practice by software developers and vendors of preparing a document that describes how well a product or service complies with various accessibility standards. This document aims to help buyers make strategic, informed, data-driven decisions when shopping for accessibility solutions in a crowded marketplace.
The document clearly states the various accessibility features available and highlights the areas where they are deficient. The mark of a superior service provider is that the accessibility document must be authentic and credible. Hence, this document will be crucial in helping buyers make the right decision.
In education, VPAT certification plays a vital role in helping educators choose solutions relevant to learners with disabilities and learning challenges.
VPAT Certification: What is it?
VPAT, or Voluntary Product Accessibility Template, is a document developed by the Information Technology Industry Council (ITIC) that outlines how your ICT products meet specific accessibility guidelines. There are four versions of this certificate in its current iteration (v.2.5):
- VPAT 2.5 508 Edition: Designed to adhere to Section 508’s accessibility requirements, it is a must if you are selling to federal agencies or are entitled to receive federal funding.
- VPAT 2.5 EU Edition: Designed to adhere to the EU accessibility requirements (EN 301 549).
- VPAT 2.5 WCAG Edition: Designed to adhere to WCAG guidelines (2.2, 2.1, and 2.0).
- VPAT 2.5 INT Edition: Designed to adhere to 508, WCAG, and EN 301-549 accessibility requirements.
Why VPAT Accessibility Matters in Education?
Educational institutions are being held responsible for digital accessibility. Respecting VPAT guidelines and 508 compliance requirements:
- Lower Legal Risks: Organizations that abide by accessibility standards avoid legal action under Section 508 and other laws.
- Increases Student Engagement: Learners of all abilities receive a better experience, improving learning outcomes.
- Encourages Inclusivity: It allows individuals with physical, cognitive, visual, and aural impairments to attend online education.
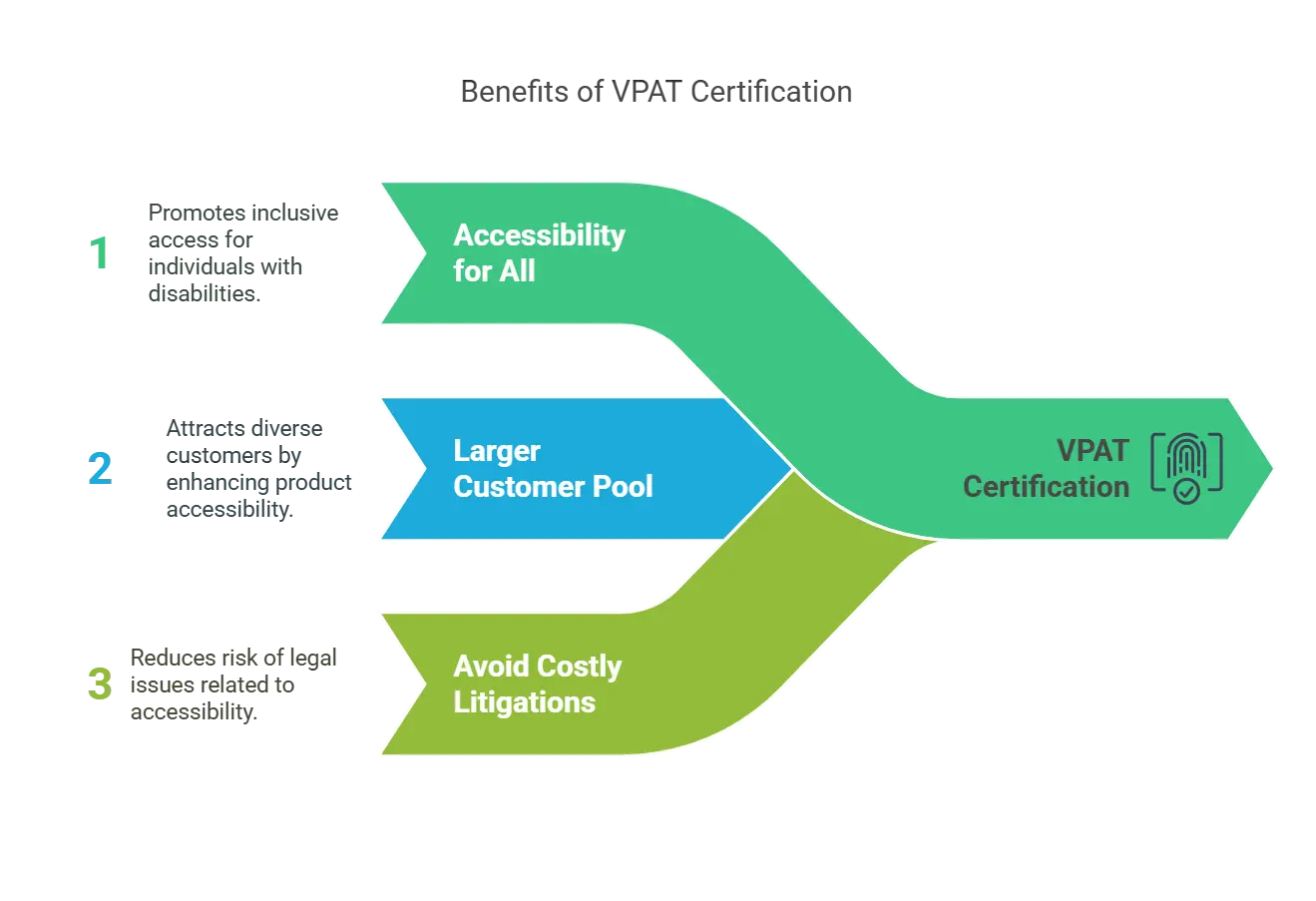
Why Should You Consider Being VPAT Certified?
There are several reasons why you should use VPAT as an EdTech Publisher:
1. Accessibility for All
According to the National Center for Educational Statistics, nearly 15% of public school students (for the 2022–23 school year) required special education services under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA). All students with a VPAT certification can equally access digital products.
2. A Larger Customer Pool
If your EDTech firm sells educational products, VPAT compliance will allow you to widen your potential customer base to include those 7.5 million students. Accessibility and inclusivity are traits that matter to today’s customers and will also significantly boost your reputation.
3. Avoid Costly Litigations
Over 3000 class action lawsuits were filed over website inaccessibility in 2022 alone. With VPAT certification, you can create accessible products and avoid potentially costly legal action. Now, let’s examine the VPAT certification procedures in more detail.
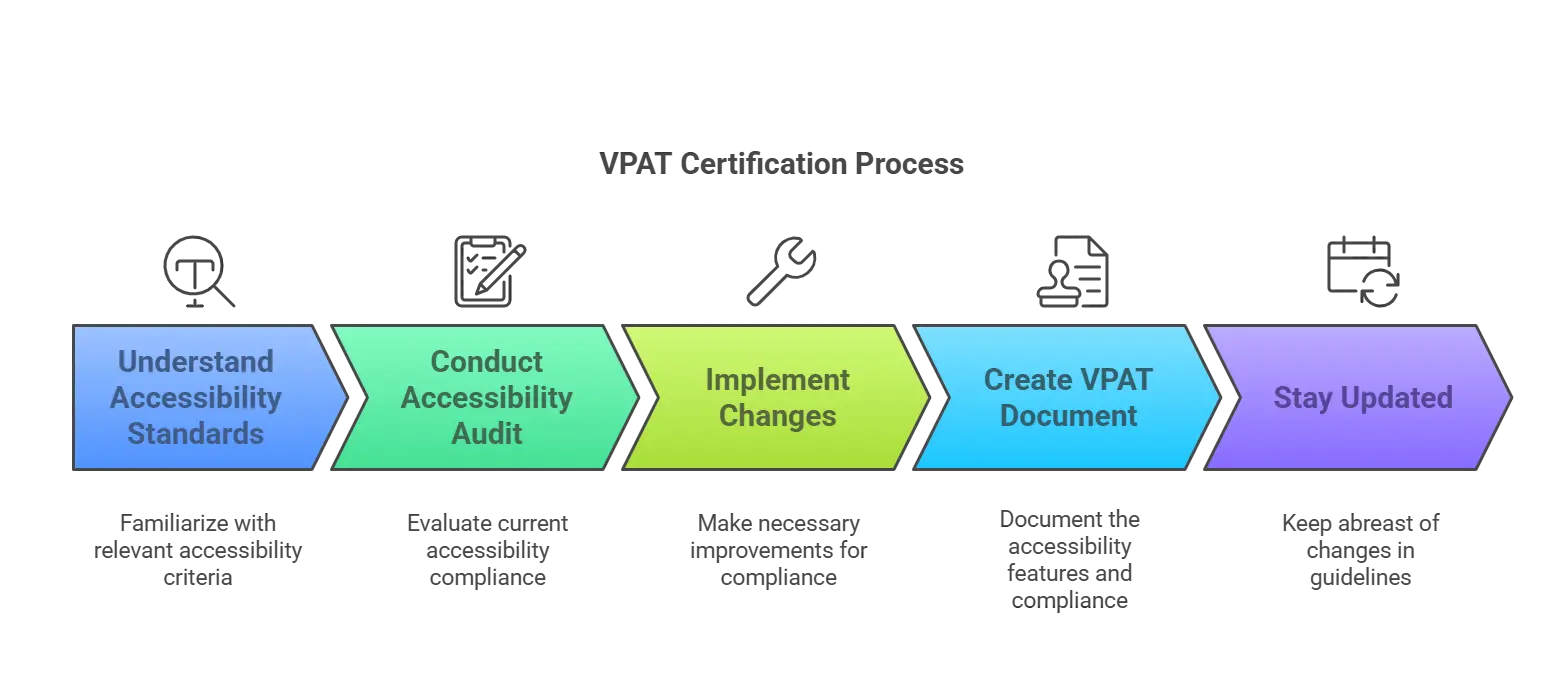
How to Get VPAT Certified?
While no formal process is set in stone to get a VPAT certification, you can follow these five simple steps to ensure you meet all the VPAT certification requirements:
Step 1: Understand the Accessibility Standards
Adhere to the pertinent accessibility standards for the region you want to target. For instance, if your EdTech platform serves a global audience in the EU, you have to abide by EN 301 549, Section 508, and WCAG.
Note: WCAG guidelines apply to all four versions of the VPAT certifications.
Step 2: Do an Accessibility Audit
Assessing your EdTech platform’s accessibility is important. You should include all of your ICTs and platforms in the audit. If you are based in the United States, refer to Section 508 as a guide.
You can use free online automated accessibility evaluation tools like Accessibility Checker. Identify any areas of improvement.
Step 3: Implement Changes to Address Any Accessibility Deficits
Make all the necessary improvements to your EdTech platform to address any accessibility deficits the audit revealed. The most common culprits include:
- The lack of alternative content (alt-text, captions, and audio descriptions)
- Lack of keyboard navigation.
- Poor color contrast
- Incompatibility with assistive technologies.
Step 4: Create Your VPAT Document
Once you have done what is needed, gather all your compliance data (what criteria you have and what you don’t) and fill out the correct version of the VPAT document. Transparency is key when adding information here.
Display your document on your EdTech platform to reflect your commitment to accessibility and inclusivity.
Step 5: Stay Updated with the Guidelines
Accessibility guidelines are constantly being updated. Stay up-to-date with them, retest your platform for compliance, and keep updating your VPAT certificate as and when needed.
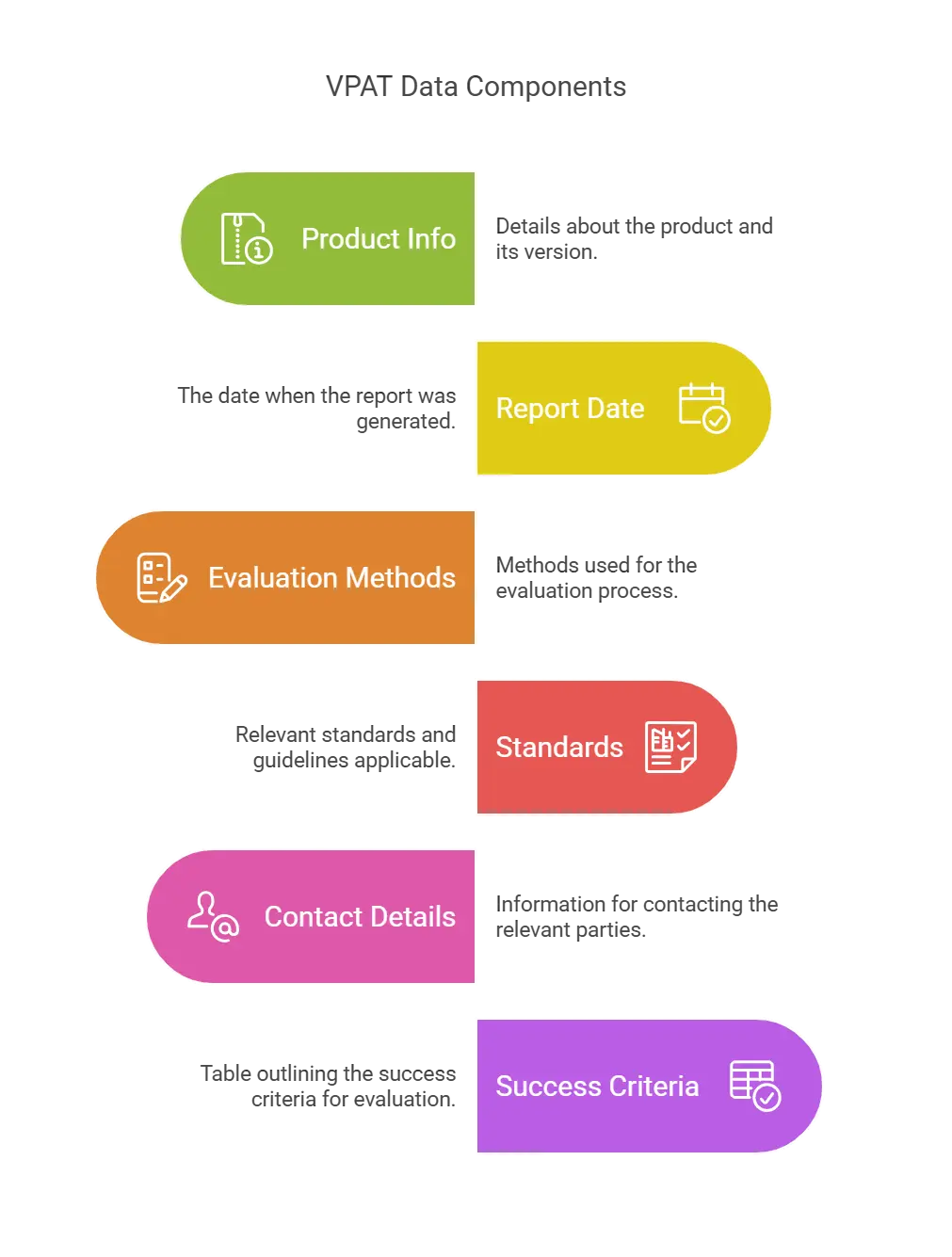
Decoding VPAT Data
Typically, vendors and product makers list the following details in the VPAT accessibility document as a way to educate buyers:
1. Product Name and Version
The document clearly states the product’s name and version. This information helps the buyer ensure that the VPAT version corresponds to the correct product version.
2. Date of the Report
This data refers to the date the VPAT was published. The report must not be older than one year, in which case the data may be outdated.
3. Evaluation Methods Used
The VPAT must offer detailed descriptions of all the various accessibility parameters that have been tested. It must also offer details on the various tools and technologies used to test the product.
4. Applicable Standards/ Guidelines
Accessibility guidelines and standards continue to be updated regularly. Various international, national, and local guidelines must be followed. For example, WCAG and Section 508 are the accepted standards that must be followed in the USA. VPAT must also state the version of these guidelines that have been adhered to.
5. Contact Information
Buyers must be able to ask detailed follow-up questions about the product. Hence, VPAT must clearly state the contact details of a company’s dedicated third-party or in-house expert. They should be easily accessible and contactable and be able to answer questions related to the accessibility aspects of the product.
6. Success Criteria Table
This table plays an important role in helping consumers understand the accessibility features of the product to ensure that they are relevant to their needs. The table has three columns as follows:
- WCAG Success Criteria: This column states all the accessibility features that WCAG perceives.
- Conformance Level: The VPAT clearly maps the product’s capability for various criteria to a scale. For instance, the documents may rate conformance as follows: ‘supports,’ ‘partially supports,’ ‘does not support,’ or ‘not applicable’.
- Remarks: The vendor can add further instructions and explanations for each criterion and corresponding conformance level.
Step-by-Step Guide to Achieving VPAT Accessibility
To create content that’s not only compliant but also accessible to everyone, follow these best practices:
1. Familiarize Yourself with Accessibility Standards
First, you have to know the relevant standards for creating VPAT-compliant education content:
- WCAG 2.0 and 2.1: The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) are divided into levels: A, AA, and AAA. For most learning resources, AA is the applicable level. Key criteria include text readability, navigation ease, and compatibility with screen readers.
- Section 508: It is a United States federal law that requires all online content which is sponsored by the state to be accessible. Even if you are in another country, Section 508 is a strong benchmark for accessibility.
- VPAT 2.0: This template clearly describes product compliance with accessibility requirements. The latest VPAT version aligns with international standards, making it relevant for organizations globally.
2. Conduct a Thorough Accessibility Audit
An accessibility audit is your starting point for identifying gaps in VPAT compliance. Use a blend of automated tools and manual testing to evaluate your content:
- Automated Testing: Tools like Hurix Digital, WAVE, and Axe Accessibility Checker can quickly detect technical issues in your code. They help you scan for accessibility problems, including missing alt text or low contrast.
- Manual Testing: Review each component manually. Experienced testers simulate real user experiences. Verify navigability for persons with disabilities and test for screen reader compatibility.
- Assistive Technology Testing: To make your content accessible to visually impaired people, utilize screen readers (such as JAWS or NVDA) and screen magnifiers.
Tip: For a more thorough audit, consider user feedback from disabled people. Their insights can reveal accessibility gaps that automated tools might miss.
3. Structure Your VPAT Report for Clarity
Your VPAT report should be clear, detailed, and easy to understand. Each VPAT document typically includes the following sections:
- Product Information: This includes the product name and version. It also gives contact details for accessibility questions.
- Accessibility Standards Summary: Specify which standards (WCAG or Section 508) your product meets.
- Compliance Level: The degree of conformity with each criterion should be explicitly stated (e.g., Fully Supports or Does Not Support).
- Detailed Section 508 Compliance: A point-by-point analysis showing how each feature meets 508 compliance requirements.
- Remarks and Explanations: Notes that clarify any areas of partial compliance, limitations, or workarounds.
A well-organized report demonstrates your commitment to transparency with your audience and partners.
4. Make Your Text and Visual Content Accessible
Text and visuals are foundational elements of educational materials. To ensure they’re accessible:
- Use Descriptive Alt Text: Provide concise alt text for all images. Avoid vague descriptions—be specific to help users understand the visual context.
- Utilize Descriptive Headings and Labels: Structure content with clear and hierarchical headings (H1, H2, etc.). This facilitates more straightforward navigation.
- Include Captions and Transcripts: Add subtitles and transcripts for video and audio content. It helps students with hearing impairments.
- Avoid Color-Only Indicators: For color-blind users, ensure that buttons or warnings use a combination of color and text indicators. For example, add an icon or text to indicate its purpose instead of labeling a button with only a color change.
- Use Simple Language: Avoid jargon or overly complex sentences. Any form of content should be plain enough for users to understand easily despite their cognitive impairments.
Making these adjustments ensures all users can interpret and engage with your content.
5. Design Accessible Interactive Elements
Interactive content like quizzes can be accessibility challenges. Here’s how to make sure these elements are usable:
- Keyboard Accessibility: Ensure that students can navigate all interactive elements using a keyboard alone. Test each component, including forms and other controls.
- Focus Indicators: Highlight fields users select with a distinct border or visual cue for easy identification.
- Label all form fields: They ought to be descriptive so that users know what to fill in the field.
- ARIA Labels: Use Accessible Rich Internet Applications(ARIA) labels to give descriptive names to buttons, links, and controls. This helps screen readers announce each interactive element correctly.
Accessible interactive content provides an inclusive experience, especially for those with motor or visual impairments.
6. Prioritize Accessible Fonts and Color Contrasts
The right fonts and colors significantly affect readability. Here’s how to optimize them:
- Font Choice: Use simple, sans-serif fonts like Arial or Helvetica. Avoid cursive or overly decorative fonts that are hard to read.
- High Contrast: Ensure sufficient contrast between text and background. For body text, aim for a ratio of at least 4.5:1.
Tip: WCAG provides a color contrast checker that can help you test and adjust the colors of your content for accessibility.
7. Keep VPAT Documentation Updated
Since digital content and software are continuously updated, so should your VPAT documentation. To maintain VPAT compliance:
- Update Annually: Refresh your VPAT annually to reflect software updates or new standards.
- Document Changes Clearly: For each update, note any adjustments or new compliance efforts in the VPAT document.
- Re-Validate with Each Major Change: Conduct a new accessibility audit whenever you change your product’s structure or functionality significantly.
Accessibility standards evolve; staying current ensures ongoing compliance.
8. Optimize Content for Multiple Devices
Learners access educational content across various devices. Make sure your content is accessible on all devices:
- Responsive Design: Your layout must adjust to different screen sizes, making it easy to use on desktops, tablets, or smartphones.
- Browser Compatibility: Test your content on popular browsers, including Chrome and Firefox. This guarantees consistent accessibility across platforms.
- Touch Screen Functionality: Ensure buttons and other interactive elements are easily clickable on touch devices.
Testing for multi-device compatibility helps you meet the needs of a diverse user base.
9. Train Your Team on Accessibility Standards
Accessibility should be a team-wide effort. Educate your content creators and developers on best practices:
- Workshops and Seminars: Host regular training sessions on VPAT compliance and WCAG guidelines.
- Resource Sharing: Provide resources, such as checklists and accessibility tools, to support team members in creating accessible content.
- Accessibility Champions: Designate team members to monitor and promote accessibility best practices within their departments.
Empowering your team with the proper knowledge ensures ongoing compliance and accessibility awareness.
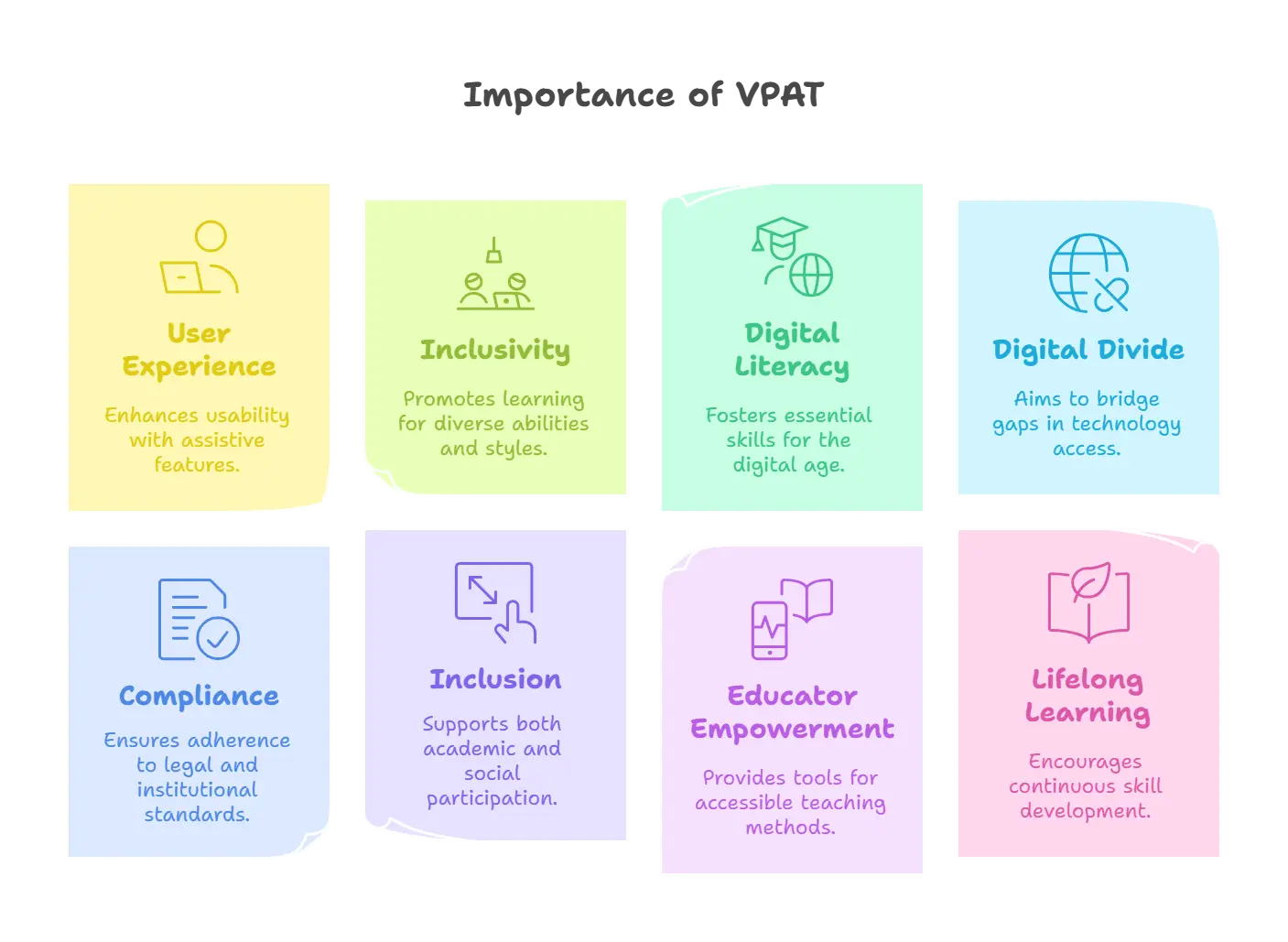
Importance of VPAT in Improving Digital Literacy for Students
Equality in education directly impacts the quality and inclusiveness of learning experiences. Here is how VPAT accessibility benefits students, educators, and institutions:
1. Enhanced User Experience Through Assistive Features
VPAT compliance includes assistive features that benefit students with different abilities and the normal crowd. For example, screen reader compatibility, keyboard navigability, text-to-speech functions, and customizable display settings are features of an inclusive interface.
Students with visual impairments can use assistive features such as text-to-speech or screen reading, while those with motor challenges can depend on keyboard navigation. By using VPAT-compliant interfaces, educators and institutes provide a navigable, inclusive platform for all students, making learning a hassle-free experience.
2. Encouraging Inclusivity for All Learning Styles and Abilities
All students show different patterns of learning. Some are visual learners, while others have auditory learning styles. Some students have particular sensory or cognitive needs. By making digital tools and resources follow the WCAG 2.0 (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) standards, institutes ensure the content is adaptable to a student’s multiple learning styles.
3. Encouraging Digital Literacy Skills
Digital literacy allows educators to navigate, evaluate, and communicate digital information effectively. Accessibility features provide seamless experiences for students to explore new platforms, adapt to changing technologies, and become independent digital users. By making websites, mobile applications, software, and other digital content accessible and inclusive, educators empower a broader learner audience.
For example, students with limited vision can benefit from an inclusive screen reading feature, while those with auditory issues can enjoy captions, transcripts, and legible fonts.
4. Reducing the Digital Divide
VPAT accessibility is crucial in bridging the digital gap, especially for students with different abilities who are often excluded from online learning. Accessible resources help every student to participate in the learning experience. When organizations remove digital barriers, they gain access to more candidates and harbor a more diverse and inclusive workforce.
Fighting for inclusivity also strengthens trust with diverse communities and displays a brand’s commitment to accessibility in digital learning.
5. Supporting Legal and Institutional Compliance
VPAT accessibility benefits students but is a key component of legal compliance for organizations and educational institutes. By following 508 compliance requirements, educators ensure equal access to information among all students.
When organizations strictly follow accessibility standards, they clearly commit to inclusivity and equality in education. This helps set a positive example for promoting inclusivity and prevents legal challenges, costly court battles, and reputational damage for the company.
6. Facilitating Academic and Social Inclusion
When organizations make informed decisions to build an inclusive ecosystem, they encourage a well-rounded educational experience for all their students.
Students are more likely to feel connected and included without constant digital barriers. This inclusion goes beyond academics, as accessible coursework encourages group projects, discussions, and extracurricular activities for students.
This approach values diversity in learning styles and builds a supportive and unified community to strengthen the educational ecosystem.
7. Empowering Educators with Accessible Teaching Tools
When educators and institutions provide accessible digital resources, they also give educators the confidence to use these tools effectively, knowing they meet WCAG 2.0 standards for accessibility. With accessible tools and features included in resources, educators can confidently engage with students with visual, auditory, or cognitive impairments.
VPAT certification allows educators to stay focused on teaching without constantly worrying about modifying content for special students or troubleshooting accessibility issues.
8. Supports Lifelong Learning Skills
Accessible digital resources prepare students for a competitive, technology-driven future. They enable students to independently navigate digital environments, improving their digital literacy and self-sufficiency. This digital inclusivity prepares students for higher education or workforce challenges, where digital literacy and proficiency are essential for performance.
How Can Educators Harness VPAT Accessibility?
When educators are evaluating solutions for their accessibility needs, they must be in a position to interpret the VPAT compliance data effectively. Here are some tips to help educators harness the document effectively:
1. Review the Document in Detail
Educational organizations must spend adequate time reviewing the document and understanding the data offered. If they have a limited understanding, it is advisable to speak to an accessibility expert to ensure that all their accessibility functionality needs are met.
2. Identify Key Functional Areas
Educators should identify the key functional areas relevant to their teaching environments. Not every VPAT section may apply equally. By focusing on critical areas—like screen reader compatibility, color contrast, and keyboard navigation—they can quickly assess whether a solution aligns with their accessibility priorities.
3. Engage with Stakeholders and Accessibility Champions
Collaborate with other educators, administrators, and accessibility champions within the institution to review VPATs collectively. Multiple perspectives lead to varied accessibility needs being highlighted and ensure that the technology supports the diverse requirements of all users, including students and faculty with disabilities.
4. Monitor and Reassess Accessibility Compliance Regularly
Once a solution is adopted, accessibility evaluation shouldn’t end.
Periodic reassessment of the product’s accessibility compliance ensures it remains inclusive as it evolves. Regularly reviewing VPAT updates can reveal any changes in accessibility features, giving educators an ongoing view of the product’s accessibility lifecycle.
Bonus: Tips for Filling Out a VPAT
Filling out a VPAT ensures that products meet accessibility standards and helps maintain transparency for students.
- Choose the Correct Version: Selecting the version that is aligned with the market and standards helps make the accessibility journey easy (e.g., Section 508, WCAG, EN 301 549)
- Gather Data: This includes collecting relevant information on screen reader compatibility, keyboard navigation, color contrast, etc.
- Complete Sections Methodically: Describing the product, indicating conformance levels, and providing explanations for each rating
- Be Transparent: This includes stating limitations and planned improvements to build brand trust.
- Conduct an Expert Review: The manual needs to be accurate and compliant
- Update Regularly: VPAT updates need to be integrated as the product evolves
Wrapping Up
Embracing VPAT accessibility is not just about ticking boxes for regulations; it’s about nurturing a welcoming learning atmosphere where every student can shine. When accessibility barriers are present, they can discourage users from engaging with meaningful digital experiences, leading to overlooked chances for connection, learning, and personal growth.
By prioritizing accessibility to digital resources right from the start, educational institutions can uplift every student, helping them build valuable skills that will lead to success in academics and future careers.
Hurix Digital is committed to improving the digital learning experience for all students and providing accessible digital solutions to organizations. We aim to help institutes and educators identify areas for improvement to create better and more inclusive learning environments.
Our team will assist you at every step of your accessibility journey, helping you engage students and improve their learning outcomes.

Vice President – Digital Content Transformation. He is PMP, CSM, and CPACC certified and has 20+ years of experience in Project Management, Delivery Management, and managing the Offshore Development Centre (ODC).