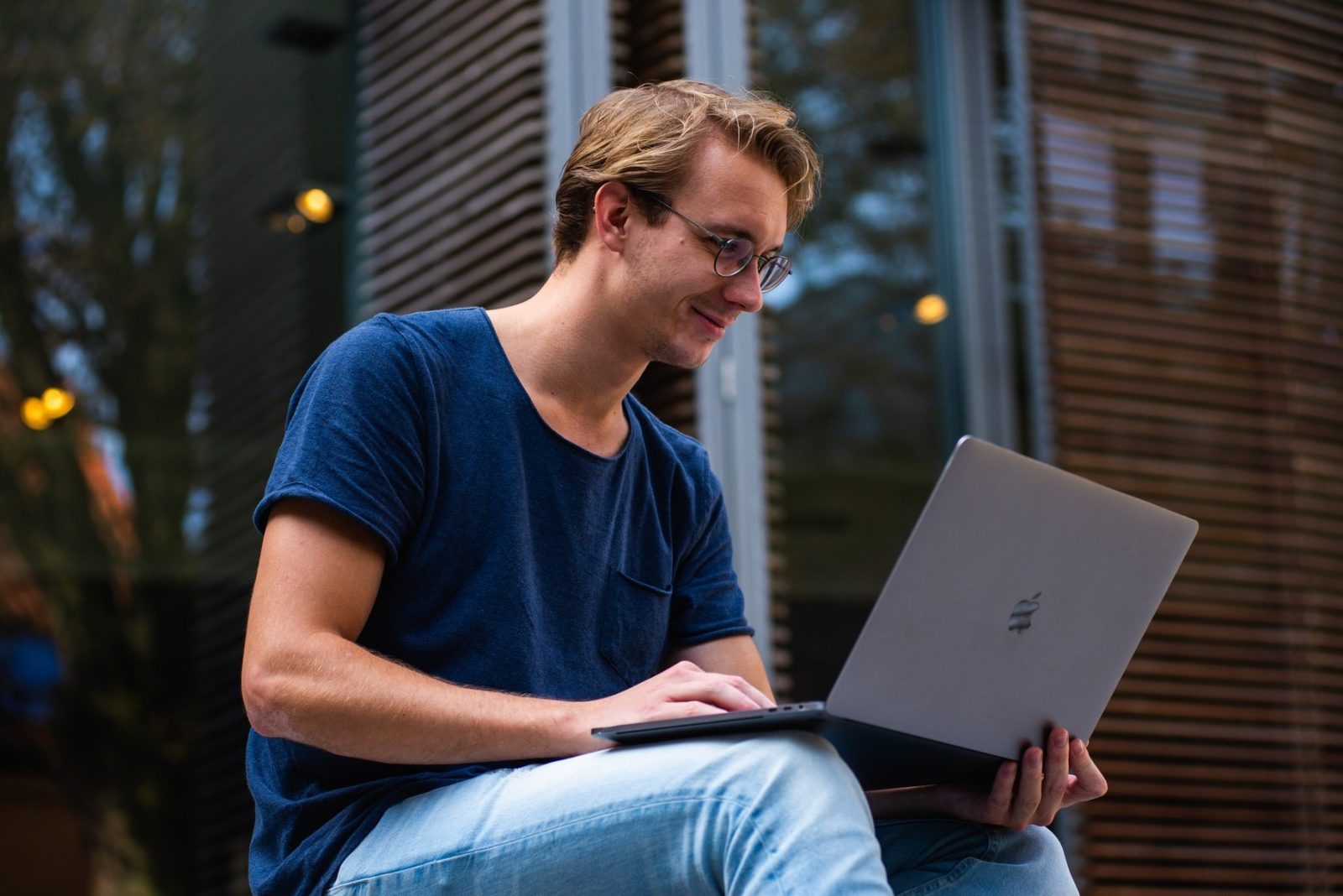

5 Ways of Online Course Development for Higher Educational Institutions
Summarize with:
Educational institutions have long focused on disbursing education and knowledge through a one-size-fits-all approach. Even though these standardized learning models simplified things for institutions and teachers, it is now recognized that they offered limited benefits to students. Traditional learning methods place the teacher in a pivotal role as the primary source of knowledge.
This guide will explore key strategies for developing more effective and engaging higher education courses.
Table of Contents:
- The Essence of Higher Education Course Development
- Importance of Student-Centric University Course Development for Colleges and Universities
- Factors to Consider When Preparing for University Course Development
- How to Design Customized Higher Education Course Development?
- 5 Ways of Higher Education Course Development and Curriculum Development for Universities
- Final Words
The Essence of Higher Education Course Development
The entire process of education revolves around the teacher disbursing information in the form of class lessons and then testing the students’ grasp of these through quizzes and tests.
Let us look at some facts related to the essence of university course development:
- The online education market is expected to reach $185.20 billion by the end of 2024. This shows the eLearning industry’s accelerated growth, which grew by 900% from 2000 to 2020.
- When undergraduate and graduate students are compared, participation in online courses seems almost equal, at 54.4% and 53.5%, respectively.
- Almost 40% of higher educational institutions reported they would raise budgets for online program development in the coming year.
- Online courses have a much higher completion rate, at 12% to 15%, in contrast to the 4% to 9% completion rate experienced in a traditional class.
Considering these facts, there has been a clear drift towards a student-centric education model in recent years, especially with eLearning gaining momentum.
This is particularly true of higher education, where online course development is focused on addressing students’ needs rather than the convenience of educational institutions or faculty members.
Also Read: Top 5 Data Modernization Strategies for Higher Education
Importance of Student-Centric University Course Development for Colleges and Universities
The key difference between a teacher-centric and student-centric education model is that the former is summative while the latter is formative. A student-focused model of learning has some obvious benefits. The foremost is that this form of education addresses every student’s individual needs and goals.
Some of the other benefits that have placed student-centric models at the heart of college course development include:
1. Faster Learning
Research indicates that studying course materials that address individual needs helps students grasp knowledge faster and improve retention. Student-centered University course development focuses on creating content for learning according to learners’ individual requirements.
It accelerates learning, as students learn faster and retain information for long periods, as their learning styles are prioritized when designing the course materials. Personalized learning experiences boost confidence in a student’s ability to learn.
2. Higher Engagement
Unlike the preceding generations, today’s youth has grown up in an era of computers, the internet, and smartphones. This inherently tech-savvy generation finds it easier to engage in online learning modules developed with their individual needs in mind rather than a one-size-fits-all classroom environment.
3. Value Addition in Educational Content
This approach also creates an opportunity for dynamic college course development, with room to improve and tweak the educational material. A student-centric model is indeed the key to making online learning optimally effective.
4. Blended Learning Environment
Student-centric course development does not remove teachers from the equation, especially in higher education. Instead, it changes their role from disseminators of knowledge to guides that can help students improve their grasp of different concepts and steer their learning in the right direction.
5. Life Long Learning
Online course development and curriculum development for universities for higher educational institutions promote curiosity and passion for learning that is beyond the classroom. Students continue self-improvement and professional development throughout their lives.
6. Bridging Learning Gaps
Traditional, one-size-fits-all education generalizes student needs and falls behind. Student-centered higher education course development identifies these gaps and supplies the additional help and resources needed by the students. This would ensure that no student falls behind.
7. Retention Rates
The more a student feels that the course teaches him to succeed, the greater the chances that he will carry through his educational endeavors. A student-centered approach helps create ownership and interest in learning, thus leading to higher retention and fewer dropouts on college campuses.
8. Diverse Learning Styles and Needs
Students come from various cultural, academic, and personal backgrounds, each with unique learning preferences. A student-centric approach incorporates flexibility in content delivery to ensure inclusiveness and accessibility for all learners, including those with special needs.
9. Deeper Faculty Student Connection
Student-centered education creates effective relationships between teachers and students. Teachers who understand, identify, and meet their students’ unique needs work to build trust and rapport. This creates a cohesive learning environment that enhances both teaching and learning processes.
Factors to Consider When Preparing for University Course Development
Developing a higher education course development demands much thought and deliberate choice to meet student needs.
Here are some of the critical factors to go through when preparing for online course development and curriculum development for universities:
1. Consider the University’s Mission and Objectives
Every course should reflect the broader goals of the higher educational institution. In designing the curriculum, the course outcomes must relate to the institution’s mission, vision, and strategic priorities. This helps ensure continuity in academic offerings and supports the institution’s reputation for quality education.
2. Relevance to Industry and Global Trends
This will ensure that students gain up-to-date skills and knowledge in industry applications. Interaction with industry stakeholders during university curriculum development would give insight into emerging trends and prepare the students to face real-world challenges.
3. Course Structure and Delivery Format
The course structure needs to balance the theoretical foundation and its practical application. More specific requirements for online course development include modular designs, multimedia, and interactive components to motivate learners.
Hybrid models of just-in-time scheduling with online and on-campus requirements should maximize flexibility without compromising content quality.
4. Accreditation and Academic Standards
Academic and accreditation standards are essential for university course development. Higher education institutions must ensure that courses comply with credit hours, attach to an assessment policy, and maintain quality benchmarks.
5. Pedagogic Approaches
Using appropriate teaching methods is essential. Contemporary higher education focuses on active student learning, cooperative projects, and hands-on experiences. Creating an online course can use adaptive learning technologies, online forums for discussions, and virtual labs to create an interactive learning experience.
6. Technology Integration
Incorporating technology into courses, whether through an LMS, virtual classroom, or the utilization of AI-driven tools, will improve course delivery and student engagement. When developing online courses, this means having robust technical infrastructure, user-friendly platforms, and cybersecurity measures protecting students’ data.
7. Inclusivity and Accessibility
Developing an inclusive curriculum for universities will ensure that courses suit diverse students with disabilities.
Language and cultural sensibility are essential aspects to consider, as are the provision of resources for a variety of learning styles. Accessibility tools such as closed captions, screen readers, and flexible deadlines are imperative in online course development.
8. Assessment and Evaluation Strategies
Sharp examination techniques are necessary for monitoring and evaluating student progression and course effectiveness. Concurrent formative and summative evaluations of learning outcomes should be conducted. In online courses, tools such as quizzes, peer reviews, and immediate feedback provide continuous engagement and progress tracking.
How to Design Customized Higher Education Course Development?
Unlike the K12 level, higher educational institutions are fundamentally more diverse, blending different subjects, streams, and specializations. How can institutions deliver customized college course development in such an environment that caters to each student’s needs?
Two key models have emerged as a viable solution to this complex situation:
1. Adaptive Learning
This model leverages the scope of eLearning to cater to every student’s unique needs. By making the course curriculum dynamic in nature, teaching methods are adapted to students’ individual needs and abilities based on their interactive experiences, responses to questions, and tasks. This approach makes online learning central to the process of imparting and receiving education.
2. Experiential Learning
This is a relatively new concept that seeks to improve traditional methods of education rather than defy them. This model places the choice of exploring the most well-suited learning options with the students.
Based on this choice, the teacher curates a learning environment designed to guide the students toward the goal they seek to achieve. This method’s objective is to help students internalize the lessons rather than superficially learn for the sake of exam grades.
Also Read: Future-Proofing Higher Ed: Scalable IT Infrastructure Solutions
5 Ways of Higher Education Course Development and Curriculum Development for Universities
Here are 5 ways in which you can implement a student-centric approach to college course development:
1. Analysis-Based Course Development
This approach can be followed as the gold standard for student-centric college course development. The software assesses a student’s skill sets, abilities, and limitations, and this information is then integrated with a learning platform to tweak lecture structures, information, questions, and assignments according to the identified individual abilities.
The effectiveness of the platform is further bolstered by automated study plans designed to improve students’ performance and boost their confidence. This rendition of adaptive learning has proven especially successful in professional courses and entrance exams.
2. Integrated Structures of Learning
Another effective spin on the adaptive learning model is adding value to online learning through integrated structures that work to bridge the gap between students and their instructors.
This system specializes in creating a curriculum and lesson plans catering to individual and group needs. Tech tools are used to collect student data that helps in understanding their levels of comprehension, both as individuals and as a group.
Then, the curriculum for a particular subject matter is packaged together, leaving room for customizing it according to each student’s individual learning style. This method keeps a student-centric approach at its heart while creating a standardized form of learning, making it a win-win from both instructional and administrative points of view.
3. Activity-Based Learning
If you thought activity-based learning belonged to the K-8 level, this adaptation of experiential learning might make you want to rethink and re-strategize your college course development process.
As the name suggests, this model relies on a range of robust activities to keep students engaged in the course curriculum while providing instructors instant insights into their abilities and levels of learning.
The activities, which range from simple quizzes to engaging games, can be tailored to the needs of each student. If a particular assignment doesn’t appeal to an individual or group of students, they can simply choose another or have it tweaked as per their preferences.
4. Entertain and Engage
This is another model based on experiential learning that aims to encourage brain application in different productive ways. The idea is to entertain and engage the learners through games that help improve their comprehension capabilities to serve the end goal of internalizing the curriculum for the long term. This model is bolstered through two extremely useful elements – a research-based authoritative curriculum and the ability to track students’ performance at all times.
5. Predictive Learning
This student-centric approach to college course development uses AI tools to align a learner’s abilities with the curriculum while tracking their progress and potential risks. It is especially valuable for colleges and universities, as it enables the creation of performance-driven course materials while preserving core aspects of traditional classroom learning.
Predictive learning utilizes software to predict student performance, assess skills, and personalize content. It helps close gaps in the learning process, ensuring a more tailored and effective educational experience.
Final Words
Researchers, educators, and colleges and universities are constantly working to improve the quality of education to create a future-ready generation. As technology advances, there are many different ways and means to attain that goal.
Irrespective of which method you choose, student-centric learning will most likely be the future of learning styles. As such, it is wise to embrace that change by overhauling your college course development approach.
If you’re interested in exploring how to integrate these innovations into your curriculum, Hurix Digital can help. Our experts can guide you in creating impactful online courses and developing effective curricula tailored for higher education. Curious to learn more? Our team is ready to support you every step of the way.
 A Space for Thoughtful
A Space for Thoughtful 



