
Step Into the Future of Education with AR and VR!
AR and VR in Education (Virtual reality and augmented reality) help students in higher education by boosting motivation and interest, improving comprehension and retention, encouraging teamwork and communication, and building skills and competencies.
Owing to huge demand, the market for VR in education is expected to reach $28.70 billion by 2030, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 30.7% from $4.40 billion in 2023.
With AR and VR, education becomes more tailored to individual students and accommodates diverse learning styles. This shift towards personalized and interactive learning experiences is expected to enhance student motivation and overall academic performance.
In this blog, we will explore the key role of virtual reality and augmented reality in education and how they are reshaping the learning landscape!
Table of Contents:
- What is Augmented Reality (AR) in Education?
- What is Virtual Reality (VR) in Education?
- Top Use Cases of AR in Education
- Case Study on How AR in Education Improve Learning Outcomes
- Is AR Just a Distraction?
- The Bottom Line
What is Augmented Reality (AR) in Education?
Augmented Reality (AR) is a multifaceted suite of technologies that help students see a crucial aspect of the world using gadgets like tablets and mobile phones that gather data from their surroundings. By increasing student engagement and expertise, augmented reality (AR) in education enhances the learning environment.
In AR, cameras and sensors identify an image and calculate the separation between the two things. Users gain an understanding of the reality they see as an outcome.
Then, projection and reflection are used to incorporate virtual data into the users’ perspective. As a result, augmented reality (AR) combines virtual components that enhance users’ perspectives with their own.
The integration of personalized, game-based learning outside of the classroom is made possible by augmented reality learning technology for educators.
What is Virtual Reality (VR) in Education?
Virtual reality (VR) is a computer-generated simulation that modifies reality impressions. VR is a virtual world with realistic-looking objects and scenarios. With certain tech accessories, such as goggles or helmets, a person can perceive virtual realities as genuine.
Virtual reality (VR) has been used in education to help learners from different cultural backgrounds bond and understand complicated subjects because it provides immersive learning experiences in multifaceted realities.
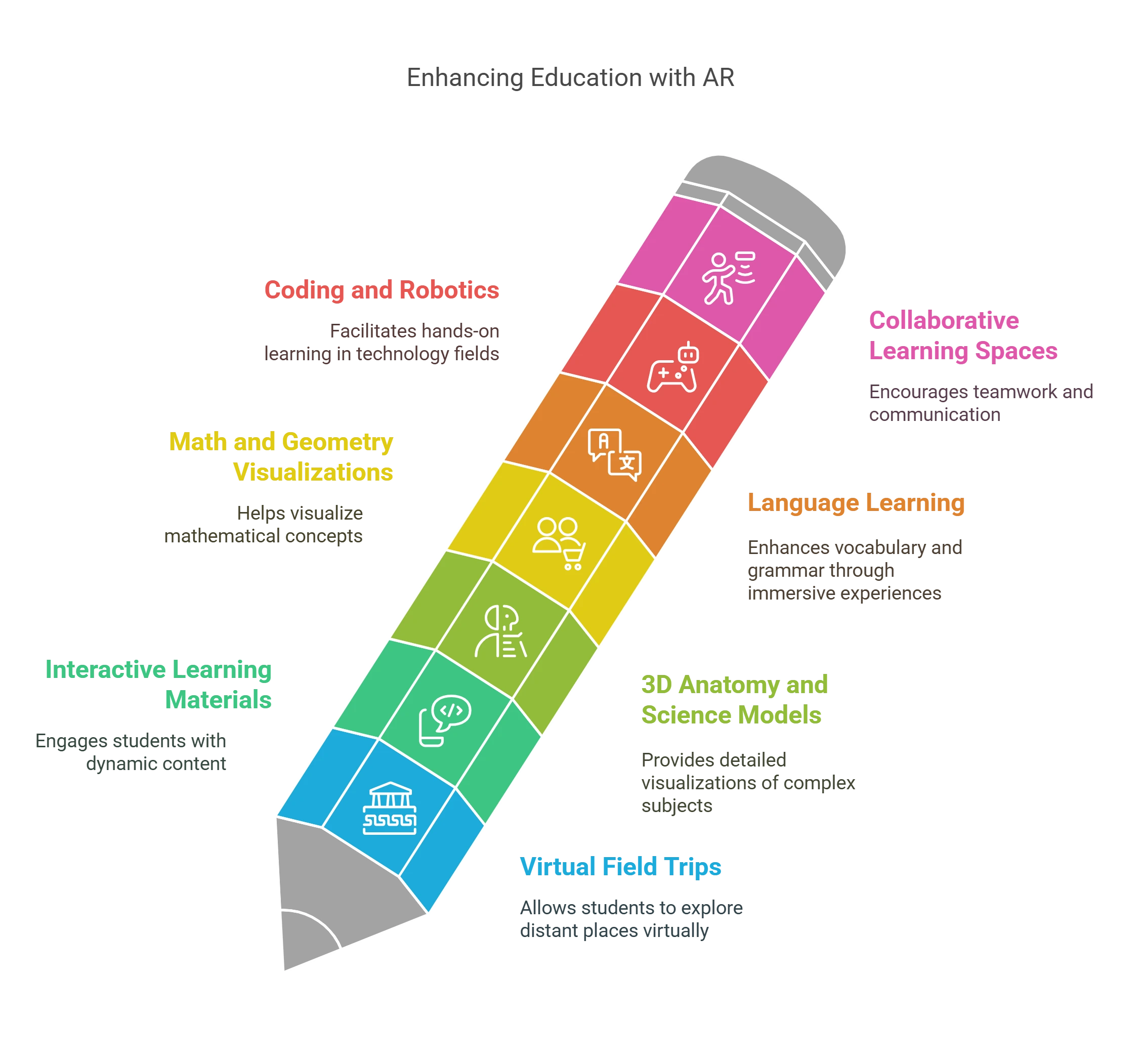
Top Use Cases of AR in Education
The traditional methods of imparting knowledge often struggle to capture the attention of today’s tech-savvy generation.
Students are growing up in a world characterized by digital interactivity, and their educational experiences should reflect this reality. AR’s ability to overlay digital content onto the physical world holds immense potential to bridge the gap between traditional pedagogy and the changing needs of modern learners.
Let’s have a look at some of the most innovative and effective use cases of Augmented Reality in education:
1. Virtual Field Trips
AR offers the opportunity to reshape traditional field trips by providing immersive learning solutions virtually.
Through AR classroom applications, students can explore historical sites, museums, and natural wonders without leaving the classroom. This will reduce logistical challenges and costs while ensuring that all students have access to enriching educational experiences.
By augmenting the real world with Virtual Reality (VR) and AR in education, virtual field trips can captivate students’ interest and enhance their understanding of subjects.
2. Interactive Learning Materials
AR in K-12 curriculum can transform static textbooks and learning materials into dynamic and interactive resources. By scanning images with AR-enabled devices, students can unlock additional content, such as 3D models, animations, and quizzes related to the topic.
Furthermore, integrating AR into learning materials brings abstract concepts to life and makes learning more tangible and memorable. This fosters a more interactive learning environment that caters to different learning styles.
Also, AR can be tailored to accommodate individual learning styles and paces. Students can explore additional content at their speed, ensuring a personalized learning experience.
Adaptive AR applications can provide real-time feedback, adapting the difficulty of content based on students’ comprehension levels.
3. 3D Anatomy and Science Models
Augmented reality in education can significantly enhance the study of complex subjects like human anatomy and scientific phenomena. By superposing 3D science models onto textbooks or physical objects, students can explore these subjects in greater detail.
For example, biology classes can utilize AR to visualize organs and their functions. This will provide hands-on and immersive learning experiences that enhance comprehension and retention of scientific knowledge.
Cai et al. introduced an augmented reality simulation system designed for junior high school students. In this system, students could manage and bring together 3D models representing tiny particles within a simulated micro-world. This method helps students understand the basics of micro-worlds. The findings indicated that when AR is integrated with inquiry-based learning methods, it leads to better learning results and positive attitudes towards the subject matter.
4. Math and Geometry Visualizations
Similar to applications in scientific studies, AR is also effective in visualizing abstract mathematical concepts and geometric shapes.
For example, in geometry, AR technology can show 3D shapes and objects in a way that makes them look more real. It can also change shapes in real-time, making learning more interesting.
Utilizing this approach, Kaufmann and Schmalstieg created a tool called Construct3D for high school students. This tool uses AR and kinesthetic learning styles to help students learn by doing and improve their ability to understand and work with space, which is an important part of learning geometry.
5. Language Learning
AR can play a pivotal role in language education by providing contextual and interactive learning experiences. Language learners can use AR apps to scan objects or texts and receive instant translations, pronunciation guides, and additional cultural information.
Kucuk et al. did a study to understand how students feel about using AR along with regular textbooks for learning English. The results showed that students liked the combination of AR and traditional textbooks.
The study also found that students performed better while needing to put in less effort to understand the topics. This suggests that combining AR with traditional textbooks could be a great way to make English learning more enjoyable and effective for secondary school students.
6. Coding and Robotics
AR can be a valuable tool in teaching coding and robotics concepts by putting virtual code elements onto physical objects. Students can see the connection between code and real-world actions and facilitate a better understanding of programming principles.
Through AR learning experiences, students can experiment with coding in a virtual space before applying their skills to tangible robotics projects, thus promoting a seamless integration of theory and practice. This hands-on and visual approach to coding education makes the learning process more engaging.
7. Collaborative Learning Spaces
AR can enhance collaboration among students by creating shared virtual spaces where they can work on projects or solve problems together.
With AR-enabled devices, students can see and interact with each other’s contributions in real time, even if they are physically apart. This fosters a sense of teamwork and allows students to collectively explore concepts or create projects in an immersive digital environment.
Collaborative AR experiences encourage communication, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills, preparing students for the collaborative nature of the modern workforce.
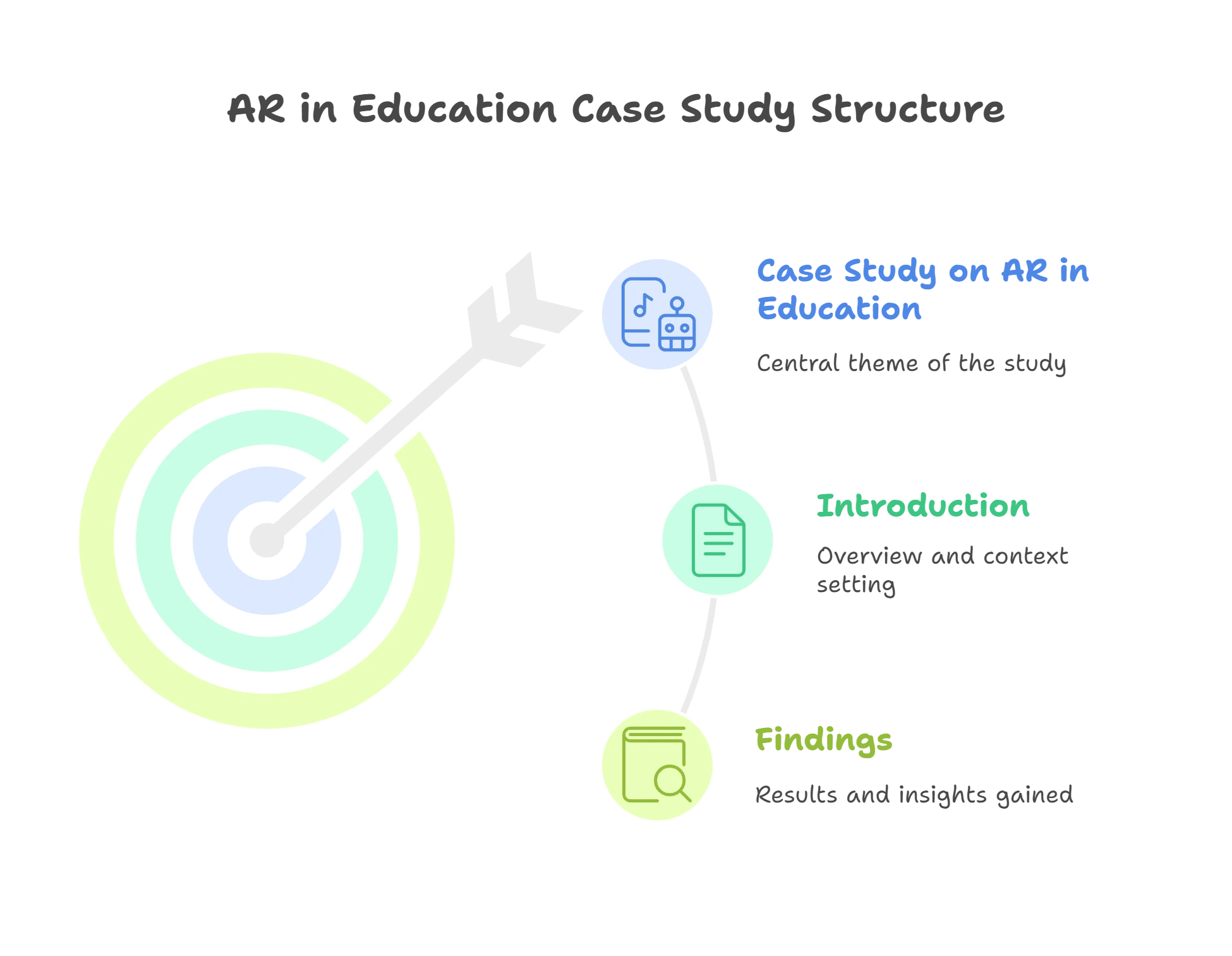
Case Study on How AR in Education Improve Learning Outcomes
A study was conducted to explore how augmented reality in education can improve learning and critical thinking for 8th-grade students. The researchers focused on how different AR designs (image/mark) interact with students’ mental capacities (high/low) and how these factors affect their learning retention (LR) and critical thinking (CT).
1. Introduction
The study involved 120 students from six schools, split into control and experimental groups. The aim was to see if AR-based digital learning could boost students’ ability to retain information and think critically. It also examined if AR impacts male and female students differently in science learning.
2. Findings
The results were clear: students who used AR showed better student engagement, learning retention, and critical thinking skills than those who didn’t. Students with higher mental capacities benefited more significantly in terms of critical thinking. Interestingly, male students’ science learning outcomes improved more with AR compared to female students.
AR technology proved to be a valuable educational tool, enhancing retention and critical thinking skills. The study suggests that future research could further explore these benefits, particularly in underserved communities, to maximize AR’s potential in education.
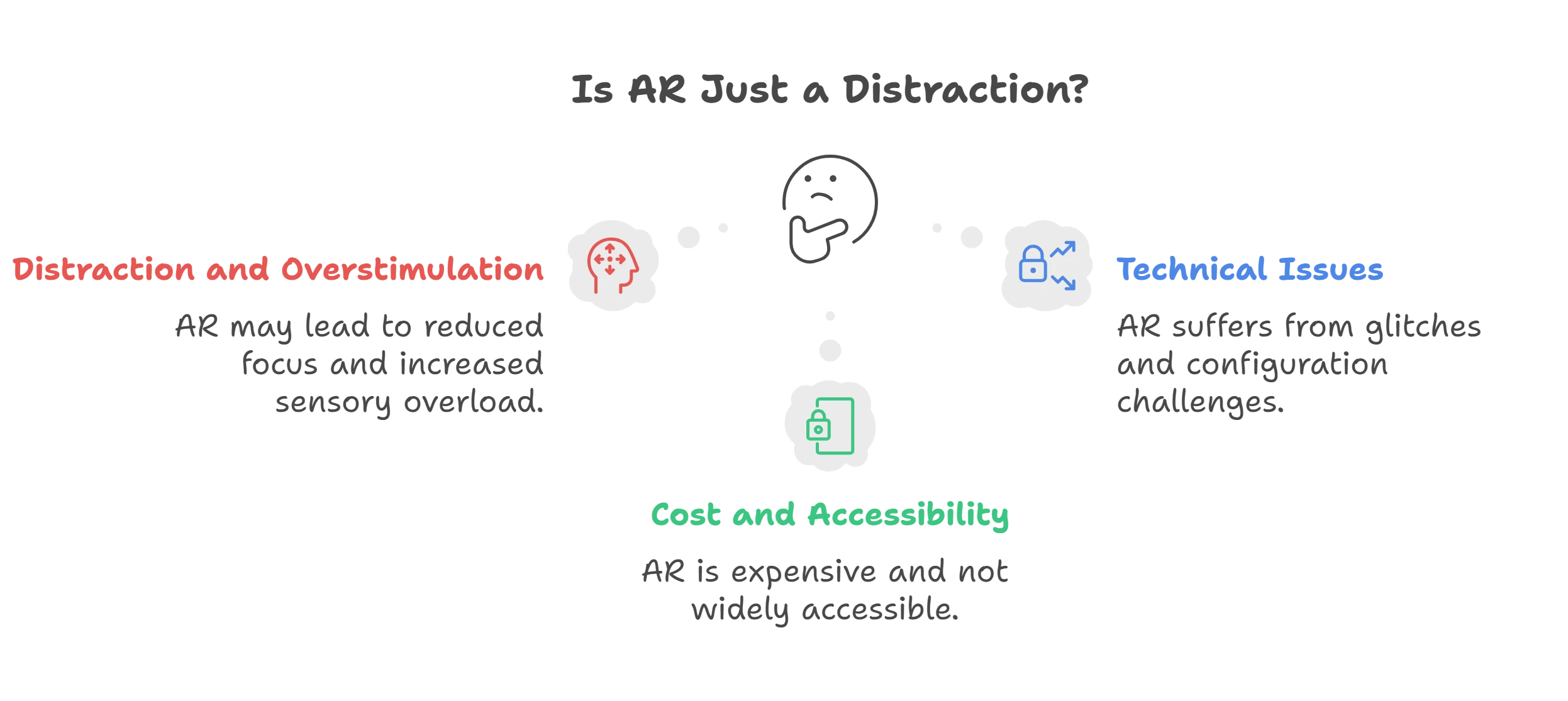
Is AR Just a Distraction?
Despite AR’s proven benefits in enhancing learning retention and critical thinking, some educators and parents worry it might be more of a flashy gimmick than a true educational tool. The concern is that its engaging and interactive nature could distract students from deeper, more focused learning.
Critics argue that while AR captures attention, it may shift focus away from fundamental skills and knowledge, making it crucial to balance innovation and traditional learning methods.
Here are a few more potential drawbacks of Augmented Reality in the education world that raise the question of it being a technical gimmick.
1. Distraction and Overstimulation
The growing concern about using AR in learning is its effect on attention-deficit behavior and overstimulation. AR features are meant to elicit positive experiences and enhance people’s interactions with a device or application, yet there is a thin line between interesting and diverting.
Participating in such AR experiences may lead students to be more concerned with the fun element than the content being taught.
Likewise, AR can also lead to some difficulties in the sensory processing of information, especially in young children. The Child Mind Institute has defined Difficulty in Sensory Processing as when children have difficulties managing the information the senses get from the environment.
The stimulating aspect of AR as a classroom technology could potentially be too much for certain learners, and the teacher would find it difficult to teach because the learners are distracted.
2. Technical and Configurational Issues
Technical problems are another significant hurdle. It’s obvious that, like any other learning technology, AR integration also relies on devices like smartphones and tablets, which must be compatible with the AR software.
Therefore, issues like software glitches, connectivity problems, and poor user interfaces can disrupt the learning process.
Consequently, these technical difficulties can frustrate students and teachers, interrupting the flow of lessons and reducing AR’s overall effectiveness as a learning tool.
3. Cost and Accessibility Concerns
Another barrier is the cost of AR-capable devices and software. High-quality AR experiences often require advanced hardware and software, which can be expensive. This creates socio-economic barriers and limits access to AR learning tools for students from low-income families or underfunded schools.
The disparity in access can widen the educational gap, making it challenging to achieve widespread adoption of AR textbooks.
The Bottom Line
While applying augmented reality is promising in increasing the motivation of learners and transforming education with the help of tools that it provides, its integration must be done rather carefully not becoming just a fancy addition. When well-chosen and well-applied, AR helps increase knowledge retention and the capacity for critical thinking.
At the same time, educators should ensure that the methods do not replace basic educational approaches but enhance them with interesting and original content. Talentedly balanced, AR can become a tool that preserves the value of acquiring knowledge.
Hurix Digital has the expertise and power to revolutionize education with tailored course development services for K12 schools and universities. Our team has full-blown experience in curriculum designing, curating engaging instructional content, and captivating media production to create unforgettable learning experiences.
Discover the difference our expertise can make in your classroom and elevate education to new heights with Hurix Digital.

Senior Vice President – Business Development
Over 25 years of experience in the edtech and workforce learning industry with strong skills in Business Development, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Strategy.







