EHS Training – Building a Safer Workplace
Summary
Most organizations struggle with EHS (Environment, Health, and Safety) maturity, but strong training can transform compliance into a competitive advantage. This article explores key strategies for integrating EHS training into corporate culture, improving safety, and driving operational excellence. With leadership commitment, cross-departmental collaboration, and innovative training methods, companies can foster a safer, more engaged workforce.
The 2024 Global EHS Readiness Report reveals a striking reality: only 3% of organizations achieve the highest level of EHS maturity, while 67% remain stuck in basic operational phases.
For executives and EHS leaders, this gap represents both a challenge and an opportunity to transform safety from a compliance requirement into a strategic advantage.
This blog will explore key strategies and leadership approaches for successfully integrating EHS Training into corporate strategy, driving cultural change, and operational excellence.
Table of Contents (Jump To):
- What is EHS Training and its Significance?
- Understanding the Importance of EHS Compliance
- Key Components of a Comprehensive EHS Training Program
- EHS Training Best Practices
- Collaborative EHS Training Programs
- Understanding Cross-Departmental EHS Integration
- Key Strategies for Effective Cross-Departmental EHS Integration
- Benefits of Cross-Departmental EHS Integration for Organizations
- Developing a Global EHS Training Strategy
- The Role of Leadership in EHS Integration
- Benefits of Integrating EHS into Corporate Strategy
- How to Embed EHS in Organizational Culture
- EHS in Organizational Culture
- The Importance of EHS Training in Crisis Management
- Key Elements of Crisis Management Training
- Developing Effective Crisis Communication Strategies
- Integrating EHS Risk Management in Crisis Scenarios
- Crisis Management Best Practices for EHS Professionals
- Importance of EHS Training for Industry 4.0
- Key Strategies for the Future of EHS Training
- The Future of EHS Training
- How Does Hurix Digital Support Effective EHS Compliance Training Programs?
What is EHS Training and its Significance?
Training in environment, health, and safety is a thorough method for ensuring workplace safety and compliance while fostering organizational excellence.
This is the information that leaders must be aware of:
1. Core Components
Environment, Health, and Safety Training includes risk assessment, compliance protocols, and safety procedures to protect employees and organizational assets. This basic element provides a systematic approach to workplace safety.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Organizations implementing structured environment, health, and safety training programs demonstrate higher compliance rates and reduced incident frequencies, which is crucial for operational sustainability.
3. Strategic Value
Integration of corporate EHS integration initiatives directly impacts operational efficiency, employee engagement, and bottom-line results through reduced incidents and improved productivity.
Understanding the Importance of EHS Compliance
Compliance with environmental, health, and safety regulations is not just a requirement that companies adhere to; it is important in any responsible business operation. These regulations cover everything from environmental laws governing emissions to workplace safety protocols and incur severe penalties if not complied with.
EHS compliance safeguards employees and the environment and ensures sustainable growth. However, it has become very challenging in this highly globalized economy, and companies must follow country-specific standards when conducting business in different countries.
Benefits of EHS Compliance:
- Reduced operational risks
- Enhanced brand reputation
- Decreased legal and financial liabilities
- Improved employee safety and morale

Key Components of a Comprehensive EHS Training Program
A good EHS training program should address the special challenges of international compliance by ensuring that all employees are conversant with applicable rules and practices.
1. Regulatory Awareness
The first step for employees to effectively comply with international EHS regulations is to understand what laws apply to their roles. They must also undergo training on local, national, and international standards and determine how they influence everyday activities.
2. Risk Management
EHS training is key to identifying, assessing, and mitigating organizational risks. Training modules should guide employees in recognizing hazards and taking preventive measures.
3. Reporting Standards
Global organizations must maintain consistent and accurate EHS records across locations, as non-compliance in reporting can lead to legal repercussions.
Training in standardized reporting practices enables better tracking, analysis, and improvement of EHS initiatives.
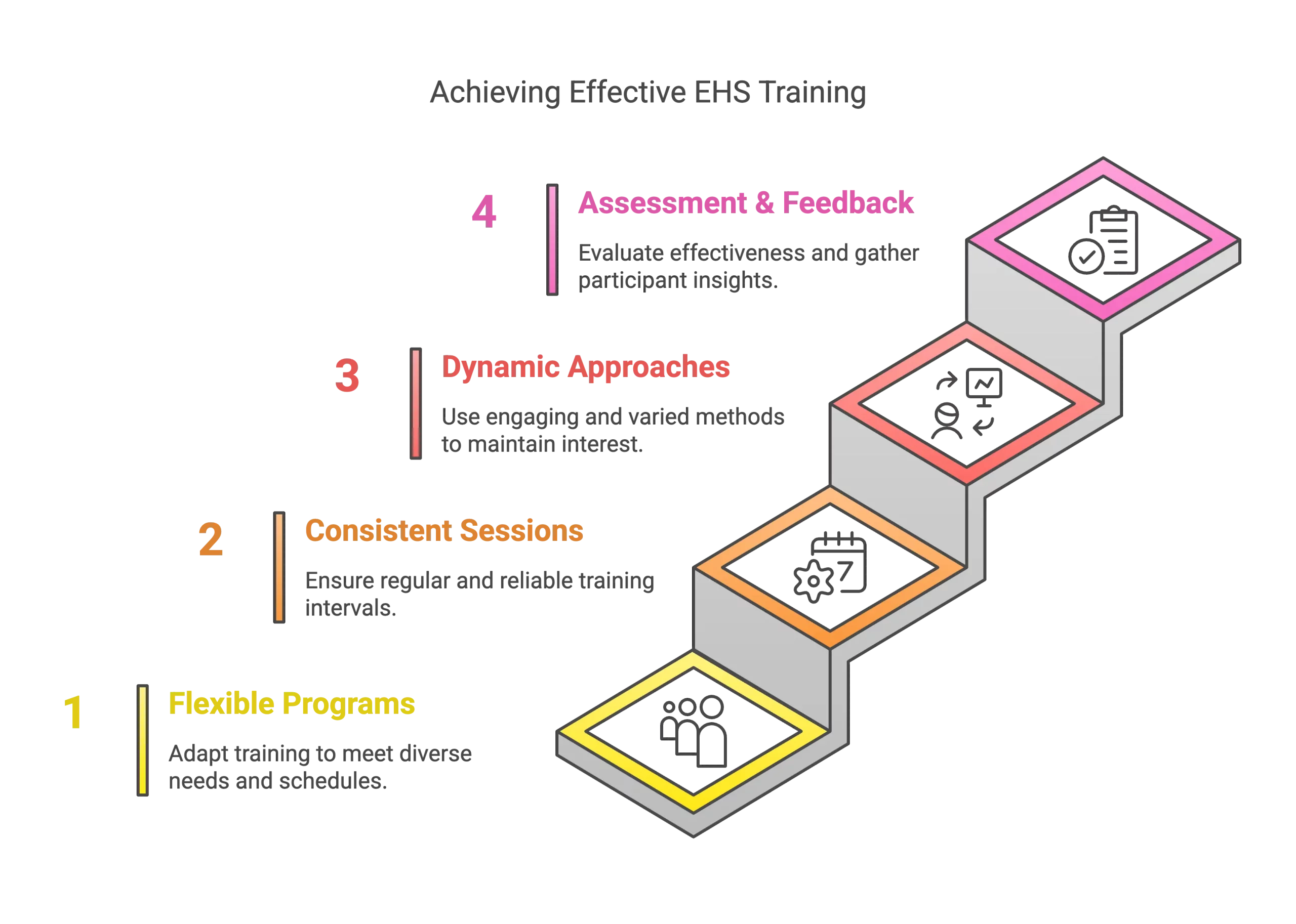
EHS Training Best Practices
Implementing EHS training best practices is essential for effectively empowering employees to tackle safety and environmental challenges. Here are some essential best practices:
1. Flexible Training Programs
Create training programs that encompass all essential elements of EHS and are customized to meet the unique needs of various departments. This helps employees grasp the distinct risks tied to their roles and how to manage them effectively.
2. Consistent Training Sessions
Hold training sessions at consistent intervals to ensure employees stay informed about the latest safety protocols and regulatory updates. Continuing education highlights the significance of EHS practices and guarantees that safety remains a top priority for employees.
3. Dynamic Training Approaches
Implement dynamic training approaches like simulations, workshops, micro-learning, and hands-on exercises to involve employees actively.
Over the last few years, as reported in Forbes, microlearning and interactive training have improved learner performances by 17% and boosted engagement by 50%. Thus, it is no surprise that your EHS training should include such impactful training approaches.
4. Assessment and Feedback
Utilize assessment tools to measure training programs’ impact and collect participants’ insights. This information plays a vital role in identifying areas for enhancement and making sure that training goals are achieved.
Collaborative EHS Training Programs
Collaborative EHS training programs bring together various departments to create and implement training that meets the organization’s shared safety requirements. These programs provide a variety of advantages and are a significant part of EHS training best practices:
- Resource Optimization: Pooling resources from different departments can create high-quality training materials and leverage diverse expertise, resulting in more comprehensive training programs.
- Consistent Messaging: A unified training approach ensures that all employees are on the same page, minimizes the likelihood of miscommunication, and consistently upholds safety practices.
- Enhanced Communication: Collaborative training creates vibrant communication channels between departments, promoting the exchange of insights and experiences that can elevate overall safety strategies.
Understanding Cross-Departmental EHS Integration
Cross-departmental EHS integration brings together the cooperative efforts of several departments inside a company to synchronize their training programs and EHS policies. Usually operating in isolation, departments handle their own EHS tasks apart from one another. This chaotic approach can lead to inconsistencies, poor communication, and inefficiencies in training and safety procedures.
By combining EHS initiatives across departments, companies create a cohesive plan that guarantees every staff member gains from consistent, comprehensive training.
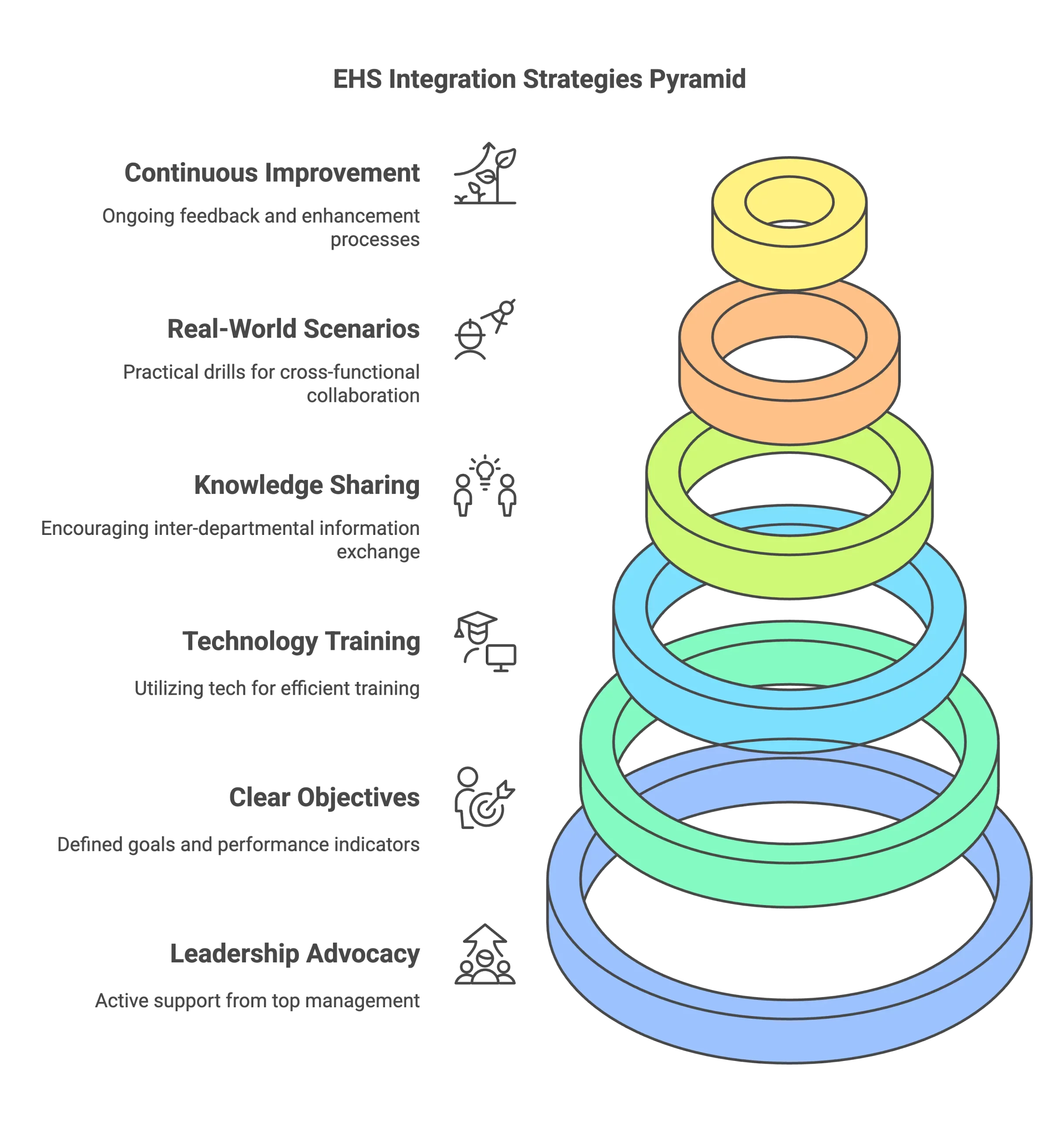
Key Strategies for Effective Cross-Departmental EHS Integration
To successfully implement cross-departmental EHS integration, a thoughtfully crafted strategy is essential to navigate challenges and attain the best outcomes. Check out these key strategies to keep in mind:
1. Leadership Involvement and Advocacy
Encouragement of a cooperative approach to EHS depends on leadership.
In EHS leadership, executives and department leaders should actively engage in training courses and promote departmental cooperation. This fosters a situation where safety is perceived as a shared responsibility rather than only the responsibility of one department.
2. Establishing Clear Objectives and KPIs
Monitoring the effectiveness and advancement of integrated EHS training projects depends on well-defined Key Performance Indicators (KPIs).
Measures of incident reduction rates, training completion rates, and compliance scores give companies insightful information to assess the effectiveness of their projects.
3. Leveraging Technology for Training Integration
Using technology such as Learning Management Systems (LMS), mobile apps, and virtual collaboration tools enhances the accessibility and integration of training across departments.
EHS training modules within an LMS can be tailored for each department while providing shared resources, metrics, and updates for a smooth experience.
4. Promoting Peer-to-Peer Knowledge Sharing
Host knowledge-sharing sessions that bring employees from different departments together to share their EHS challenges and strategies. This fosters the sharing of best practices and enables employees to gain insights from each other’s experiences, strengthening collaborative EHS practices even more.
5. Incorporating Real-World Scenarios and Cross-Functional Drills
Through cross-functional drills and simulations, staff members from several departments can understand the importance of every team member in an emergency. Including real-world events such as fire drills or hazardous material spills in training prepares staff members to work closely during genuine events.
6. Continuous Improvement and Feedback Loops
Collecting feedback from employees after training is essential for identifying inefficiencies and opportunities for enhancement.
An ongoing enhancement strategy incorporating frequent updates to training programs, driven by feedback and emerging industry standards, guarantees that EHS practices progress alongside organizational and regulatory shifts.
Benefits of Cross-Departmental EHS Integration for Organizations
Organizations that effectively implement cross-departmental EHS integration enjoy a variety of advantages, such as:
- Enhanced Safety Culture: EHS practices across departments create a culture of safety where every employee takes ownership of their own and their colleagues’ safety, encouraging a proactive approach to safety.
- Fewer Incidents and Enhanced Compliance: Ongoing training and effective communication significantly lower the chances of incidents and accidents, enabling organizations to uphold EHS regulations and avoid potential penalties.
- Enhanced Employee Morale and Involvement: When employees observe their organization committing to a cohesive strategy for their well-being, it elevates morale and involvement. Workers are more inclined to engage actively in safety training and follow protocols.
- Cost Efficiency: Sharing resources and knowledge across departments minimizes redundancy, reduces the expenses associated with duplicate programs, and allocates more funds towards innovative training solutions.
Developing a Global EHS Training Strategy
A sound approach to EHS training reflects international standards, localized content, and innovative technologies that help achieve workforce heterogeneity.
Here are some effective strategies:
1. Localizing Content
For content localization, one should first translate materials and use conditions and examples likely to reflect regional conditions. Through localization, the training will be appropriate and relevant, regardless of where you are in this world.
2. Leveraging Technology
ELearning, virtual simulations, and mobile applications could simplify EHS training.
For example, learning via mobile devices offers great convenience, as employees can access the information they need to perform EHS tasks safely at the workplace.
3. Ensuring Continuous Learning
Constant changes and new developments in EHS best practices and regulations mandate that an organization create space for continuous learning opportunities. These could be refreshers, notifications about changes in regulation, or awareness campaigns about EHS issues.
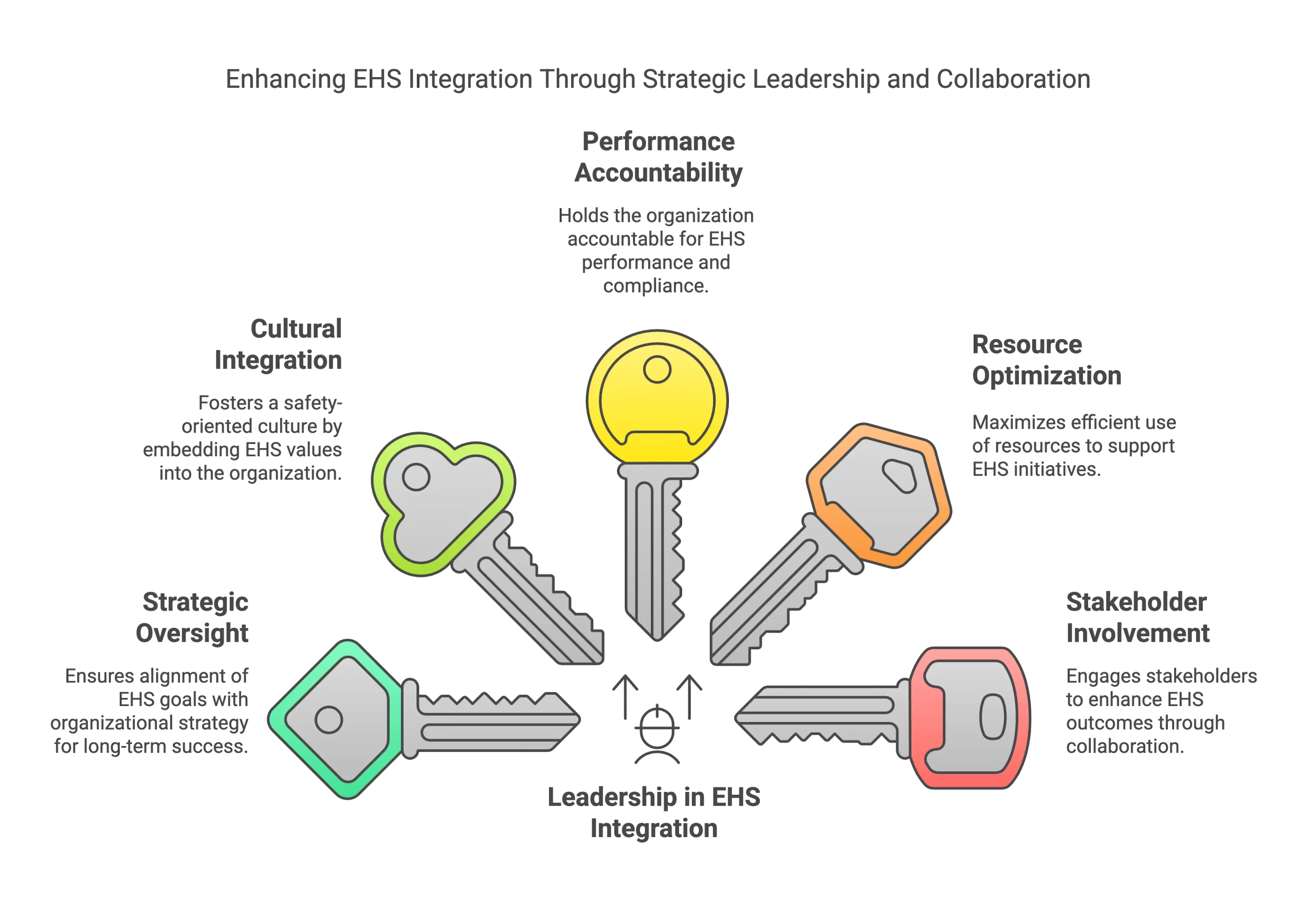
The Role of Leadership in EHS Integration
Successful implementation of the EHS programs requires a commitment of leadership and strategic monitoring. Recent studies show organizations with integrated systems achieve significantly higher maturity scores.
1. Strategic Oversight
Leadership in EHS compliance requires active participation in program development, resource allocation, and performance monitoring. Leaders should set clear safety targets and KPIs and ensure adequate funding for training initiatives.
2. Cultural Integration
Leaders must champion EHS management systems through visible commitment, regular communication, and consistent reinforcement of safety protocols. This includes conducting safety walks, participating in training sessions, and recognizing safety achievements.
3. Performance Accountability
Establishing clear metrics, reviewing outcomes, and adjusting strategies ensure continuous improvement. This involves regular safety committee meetings, incident investigation processes, and corrective action tracking.
4. Resource Optimization
Leadership should ensure the correct allocation of resources, including training materials, safety equipment, and qualified instructors to support program implementation.
5. Stakeholder Involvement
Effective leaders actively collaborate with employees, contractors, and regulatory authorities to maintain program effectiveness and address new security issues.
Benefits of Integrating EHS into Corporate Strategy
Here are the major benefits of integrating EHS into corporate strategy:
- Operational Excellence: Businesses with well-established EHS management systems report far lower incident rates and less downtime, which boosts output and lowers expenses.
- Risk Mitigation: Businesses using integrated EHS strategies report better regulatory compliance and fewer workplace accidents.
- Financial Impact: Lower insurance rates, fewer compensation claims, and significant long-term cost savings are the results of implementing a good environment and health and safety training programs.
- Storage of Workers: Companies with strong EHS programs experience higher employee satisfaction rates and reduced turnover, leading to significant recruitment and training cost savings.
- Brand Enhancement: Strong safety performance positively impacts corporate reputation, stakeholder confidence, and market competitiveness.
How to Embed EHS in Organizational Culture
Creating a safety-first culture requires a systematic approach to implementing environmental, health, and safety training across all organizational levels.
- Cultural Transformation: Businesses with the highest EHS maturity levels exhibit a strong sense of culture alignment, including safety in everyday operations and decision-making procedures.
- Employee Engagement: Successful corporate EHS integration programs convey higher employee participation rates when safety initiatives are embedded in organizational values.
- Continuous Improvement: Training programs are regularly reviewed and updated to guarantee their applicability and efficacy in tackling changing workplace safety issues.
- Cross-Departmental Collaboration: Including many departments in creating an EHS strategy promotes a more thorough methodology and greater cultural fusion.
- Leadership Communication: Consistent communication from top executives regarding safety goals and achievements reinforces EHS’s importance within the company’s broader mission.
EHS in Organizational Culture
Here’s a snapshot of how integrating EHS can reshape your organizational culture and reinforce safety values across all levels:
- Leadership Example: Executive teams demonstrating a visible commitment to safety initiatives and higher program success rates.
- Communication Framework: Regular safety communications and feedback channels strengthen program effectiveness and maintain engagement.
- Recognition Programs: By implementing incentive systems for safety accomplishments, positive behaviors are reinforced, and continued participation is encouraged.
- Employee-Driven Projects: Encouraging staff members to suggest safety enhancements and assume responsibility for specific safety procedures creates a more proactive culture.
- Onboarding and Refresher Programs: Integrating EHS training into new hire orientation and offering periodic refresher courses ensures continuous reinforcement of safety values.
The Importance of EHS Training in Crisis Management
As reported by the BCI’s 2023 Crisis Management Report, 74.4% of organizations now have senior management directly leading crisis management initiatives. Thus, the role of leadership in driving effective crisis planning and execution has never been more critical. This increased commitment underscores the strategic importance of preparedness in today’s business landscape.
Environment, Health & Safety Training is crucial for organizations to handle emergencies effectively. There are several reasons why this training is essential:
- Basis for Readiness: EHS training equips staff members with the required expertise and abilities to respond safely and efficiently in emergencies. It includes all aspects, from identifying dangers to reacting to emergencies, guaranteeing that all team members understand their responsibilities during a crisis.
- Improves Handling of Emergencies: Adequately trained personnel can greatly shorten the time needed to address a crisis, which is crucial for reducing harm and halting the escalation of dangers.
- Assisting with Regulatory Compliance: EHS training ensures that a company’s crisis management procedures meet local, state, and federal regulations, minimizing legal liabilities and possible penalties.
- Enhances Risk Management: Successful EHS training programs integrate risk evaluation methods that help businesses recognize potential crises and develop appropriate backup plans.
- Promotes a Safety Culture: Consistent EHS training helps develop a culture focused on safety, emphasizing the health of workers and the environment. Thus, safety is integrated into the organization’s core values.
Key Elements of Crisis Management Training
The organizations should have appropriate crisis management training programs so that they can respond effectively and efficiently in case of any emergency. The key elements of such a training program include:
- Scenario-Based Training: The crisis management training shall include mock drills and real-time situations that test the employees’ responses. This would enable them to tackle various types of emergencies that might arise, whether natural or due to technological failure.
- Emergency Preparedness: The training should involve specific emergency preparedness practices, including evacuation procedures and the use of emergency equipment. Understanding these procedures is necessary for ensuring safety and compliance.
- Crisis Response Planning: One requirement is that staff be trained to implement an organizational crisis response plan effectively. This includes identifying the crisis leader, understanding the flow of information, and assessing the situation. It should also define role-specific responsibility in an emergency to avoid confusion or duplication of tasks.
- Communication Strategies: Crisis communication strategies should include practical communication training during a crisis. This involves internal communications with staff, the public, and the media, focusing on conveying messages in clear and concise terms.
- Incident Management Strategies: Train employees on post-incident response, which includes incident reporting, investigation, and review of lessons learned from the incident.
- Regular Review and Updates: Introducing new risks, lessons learned from past disasters, and updated regulations require periodic review. These updates should be incorporated into the crisis management training program regularly.
Developing Effective Crisis Communication Strategies
Effective crisis communication is a major component of Environment, Health & Safety Training and is crucial for maintaining control during an emergency. Here’s why strategic communication is essential:
- Timely Information Sharing: Effective communication ensures timely information flows to the parties at different levels for relevant decision-making.
- Limiting Misinformation: Accurate and reliable messaging can avoid perpetuating rumors and misinformation, exacerbating the situation, and hindering response efforts.
- Public Trust: An organization should communicate transparently during crises to maintain the trust and confidence of internal and external audiences.
- Compliance with Regulations: Effective communication strategies are needed for EHS regulations to ensure all involved parties understand emergency procedures clearly.
- Improving Response Coordination: Clear communication helps teams and departments work together more effectively, enhancing the overall success of crisis response efforts.
Integrating EHS Risk Management in Crisis Scenarios
Integrating EHS risk management into crisis scenarios enhances resilience and safety. Here’s how risk management practices can be effectively adapted:
- Risk Identification: Identify possible crises relevant to the institution’s circumstances beforehand. These situations involve acts of nature, technological malfunctions, or the release of harmful chemicals.
- Vulnerability Assessment: Evaluate the organization’s vulnerabilities that may worsen during a crisis. This stage assists in setting priorities for responding to situations according to their potential effects on health and safety.
- Strategies for Reducing Risks: Create and execute plans to decrease known risks. This could involve strengthening infrastructure, upgrading fire safety systems, or enhancing cyber security measures.
- Emergency Response Plans: Customize emergency response plans to focus on the particular hazards that have been identified. Plans need to outline specific steps to be followed in various crises.
- Training and Drills: Based on the risk management plan, regularly train staff on their roles during a crisis and conduct drills to ensure everyone knows how to act swiftly and efficiently.
- Continuous Review and Adaptation: Post-crisis reviews are crucial. Analyze the effectiveness of the risk management strategy during the crisis and adapt plans as necessary to address any shortcomings.
Crisis Management Best Practices for EHS Professionals
Comprehensive planning, regular training, and stakeholder engagement are vital in crisis management. Notably, about 80% of companies now report having a centralized crisis management process. The most effective strategies often combine centralization with regional autonomy, allowing for tailored responses that consider local nuances.
For EHS professionals looking to enhance their crisis management capabilities, here are best practices that are critical for effective crisis management:
- Comprehensive Planning: Develop thorough crisis management plans that address a wide range of potential emergencies. Ensure these plans are specific, actionable, and easy to understand.
- Regular Training and Drills: Conduct regular training sessions and simulation drills to keep the crisis response team well-prepared. This helps to reinforce procedures and clarify roles under the pressure of an actual event.
- Engage Stakeholders: Engage them by keeping them informed throughout the crisis planning and response process. This involves leadership, staff, nearby first responders, and governing agencies.
- Update and Revise Plans: Continuously revise and update crisis management plans to reflect new vulnerabilities, technological advances, or changes in the regulatory imperatives.
- Leverage Technology: Use modern technologies, such as advanced emergency notification systems or crisis management software, to enhance communication and coordination.
- Review After Incident: Perform a detailed post-incident review to identify the efficiency of the response. Use this feedback as a continuous process to improve plans and training.
Importance of EHS Training for Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR), refers to businesses’ innovative use of technology to transform their product design, manufacture, and distribution.
EHS training in the traditional manufacturing industry covered aspects such as safety protocols for operating heavy machinery, policies related to harassment in the workplace, and safe handling of processes and equipment.
However, today, aspects such as mental health, secure adoption of tech-enabled solutions and software, digitally interconnected equipment, and absolute compliance with evolving regulations are equally important.
Thus, a mix of physical, emotional, and digital safety and EHS compliance in Industry 4.0 has emerged as top priorities for organizations in the manufacturing sector today.
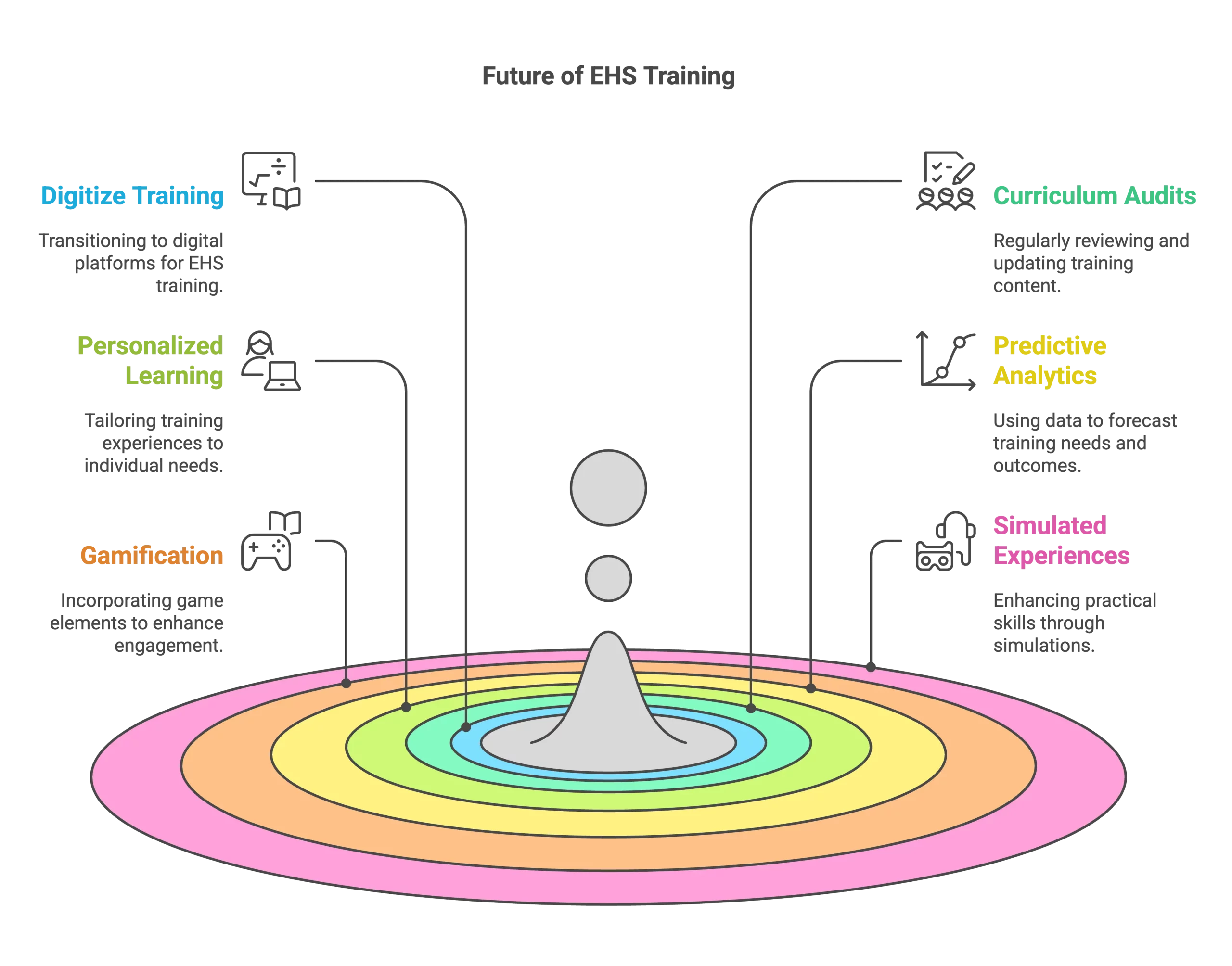
Key Strategies for the Future of EHS Training
Organizations can consider implementing the following strategies to upgrade their workforce training for Industry 4.0:
1. Digitize the Entire EHS Training Process
Interactive eLearning is the way forward for superior EHS training for Industry 4.0. Organizations with a competitive edge are advised to transform learning experiences by digitizing the entire training workflow.
For instance, adopting a superior automated Learning Management System (LMS) can help organizations seamlessly onboard recruits, deploy new learning resources quickly, and build an agile learning culture with ease and cost-effectiveness.
By adopting this approach, workplaces can offer workers access to on-demand, multi-media learning experiences. They can boost higher engagement and superior learning outcomes.
2. Introduce Regular Curriculum Audits and Upgrades
The first step for organizations is to audit their training curriculum and upgrade it on an ongoing basis. This approach makes it easy for workforces to access new knowledge and skills related to safety regulations, new technologies, industry techniques and equipment, and policies that impact their work.
3. Curate a Personalized Learning Experience
One of the most important trends in the future of EHS training is that organizations can now build customized learning experiences for every worker based on their unique learning needs and preferences.
By using AI in EHS training, organizations can completely automate the personalization process, turning documents into micro-lessons within seconds and without human intervention. In turn, organizations can run high-impact EHS training cost-effectively and with fewer resources.
4. Harness the Power of Predictive Data Analytics
Another strategic use of AI is that organizations can harness this technology to evaluate large EHS training-related data sets. AI can identify key trends by reviewing incident reports, safety audit findings, inspection logs, and other sources, turning them into insights for improved training strategies.
Organizations can forecast future challenges based on historical data. They can equip workforces with the proper training to boost learning effectiveness and preparedness for the future.
5. Introduce Gamification in EHS Training
Most workforces consider EHS training a very serious subject, and keeping up engagement can prove challenging. However, introducing gamification elements such as challenges, rewards, progress bars, feedback, spot tests, and leaderboards can transform the learning experience by raising engagement levels. Thus, gamification is emerging as a key strategy for EHS training.
6. Boost Practical Skills with Simulated Live Experiences
Enabling skill-building in live environments will be a significant component in the future of EHS training. Professionals must be allowed to practice various skills in diverse conditions without the risk of failure and injury and without their employers incurring financial losses.
This is where technologies such as augmented and virtual reality in EHS training can be game changers. Workers and team leaders can simulate a variety of scenarios to practice and hone skills individually and as a team.
The Future of EHS Training
The ability to work in a safe, secure environment is an essential pillar of success for any sustainable manufacturing business. Workers must follow important guidelines to ensure their safety and that of their co-workers and environments.
However, safety rules have changed significantly over the last five years due to technology. Today, a growing number of organizations operate in multiple geographies and work modes. For instance, workforces may operate on-site, in a hybrid environment, or from home.
Many workers are using technology via digital platforms, tech-enabled machinery, AI wearables, and other touchpoints. Companies must consider all these shifts and equip workers with the necessary tools and knowledge to ensure optimal safety and security.
How Does Hurix Digital Support Effective EHS Compliance Training Programs?
A strong EHS training program covers regional variances, language obstacles, and changing regulations, enabling organizations to achieve top-tier compliance globally. Companies that engage in thorough, continuous EHS training can confidently and effectively manage the intricacies of foreign regulations.
At Hurix Digital, we understand the complexity of global EHS compliance and have tailored solutions for companies that want to deal with the issue. Our experts work to design EHS training programs that are customized and engaging and utilize cutting-edge eLearning tools for seamless content delivery and real-time tracking.
Talk with us to learn how we can help you support your EHS training requirements and enable your global workforce to shine at the challenge of navigating international compliance today!

A highly enthusiastic and motivated sales professional with over twenty five years of experience in solution selling of training-related applications and services. Maintains an assertive and dynamic style that generates results. Ability to establish long-term relationships with clients built on trust, quality of service and strategic vision. Specializes in financial services, higher ed, publishing and government in the areas of learning and development.