
Accessibility Regulations – Making Publishing More Inclusive
Anyone in the publishing industry understands that juggling multiple projects, especially with tight deadlines and accessibility regulations, is a Herculean task.
Editors often feel pressured to rush through tasks to meet these deadlines, which can compromise accessibility guidelines.
Although deadlines may feel like pressure chambers, they are essential for maintaining a streamlined editorial workflow, ensuring accessibility in publishing, and maintaining accessibility regulations.
Managing multiple deadlines and ensuring inclusive compliance are followed is like walking a tightrope. Creating a perfect balance takes resilience and years of practice.
This article explores the typical obstacles to reaching complete accessibility in the publishing sector and offers solutions to resolve them.
Table of Contents:
- Accessibility in Publishing
- Understanding Reading Disabilities
- Understanding Accessibility Regulations
- Common Roadblocks to Accessibility in Publishing
- Strategies to Overcome Accessibility Barriers
- Why Do Accessibility Guidelines for Publishing Matter?
- Implementing Accessible Content Creation
- The Value of Accessibility Training for Publishers
- Striking a Balance Between Deadlines and Accessibility in Publishing: Practical Tips for Editorial Managers
- Tools for Ensuring Publishing Accessibility
- Wrapping Up
Accessibility in Publishing
In publishing, accessibility makes books, papers, websites, and other published items available and usable by persons with disabilities. According to the Accessible Books Consortium, about 10–15% of people have some sort of print impairment. The objective is to produce material that everyone, regardless of ability, can access.
Inclusive publishing practices guarantee that every reader—including those with disabilities—can access and enjoy materials. These methods not only increase the audience base but also follow moral and legal guidelines. Publishers are increasingly realizing, as knowledge increases, the importance of including accessibility in their procedures.
Understanding Reading Disabilities
Reading disability, more popularly known as print disability, is any condition that prevents an individual from reading printed material. It could be visual, physical, perceptual, developmental, cognitive, or even a learning disability that puts them at a disadvantage.
A person with a print disability cannot normally access traditionally printed materials that their healthier counterparts have the liberty to take for granted. This denial of access to information and resources sets them back in their journey of life. It subjects them to more struggles that can be prevented by enhancing digital publishing accessibility.
People with print disabilities require accessible eBook formats and assistive technology for reading and understanding text, whether in physical or digital formats. With the advancements in technology today and the incorporation of AI into publishing, it is possible to create an accessible design for books to make reading more equitable.
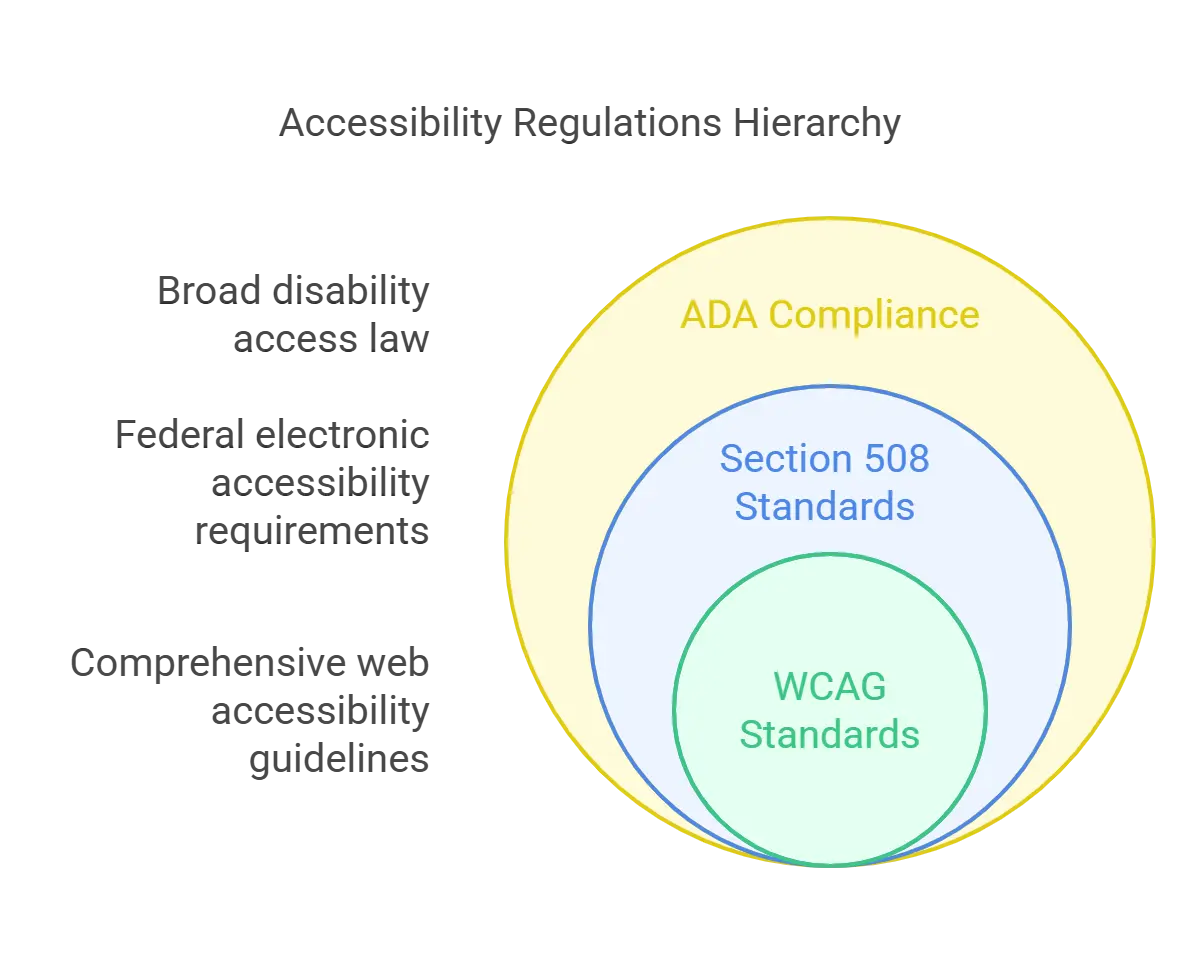
Understanding Accessibility Regulations
Accessibility regulations are important for digital content to be accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. Navigating these rules is crucial for publishing professionals to ensure compliance and inclusiveness.
Here are the particular guidelines that define accessibility in digital publications:
1. ADA Compliance
Publications and other digital information must be available to people with disabilities, according to the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). For a Director of Publishing, ensuring digital formats work with assistive technology like screen readers and visual displays.
Maintaining compliance with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) rules improves diversity and reduces legal risks related to accessibility regulation, which have surged in recent years.
2. Section 508 Standards
Federal agencies should make their electronic and data tech accessible to people with disabilities by Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act. This standard applies to any digital material that these organizations produce.
It also acts as a manual for publishers in the private sector. Despite their disability, ensure digital material is accessible to all users. Compliance with Section 508, which, in exchange, supports fair access to information and services across platforms and devices, makes this easier.
3. WCAG Standards
A complete collection of rules for improving the accessibility of web content is provided by the Web Content Accessibility Rules (WCAG). Globally recognized and completely used, WCAG standards offer a strong foundation for document accessibility in the publishing sector.
Following WCAG standards improves the overall user experience, search engine optimization, compliance with international accessibility requirements, and suitability for those with disabilities.
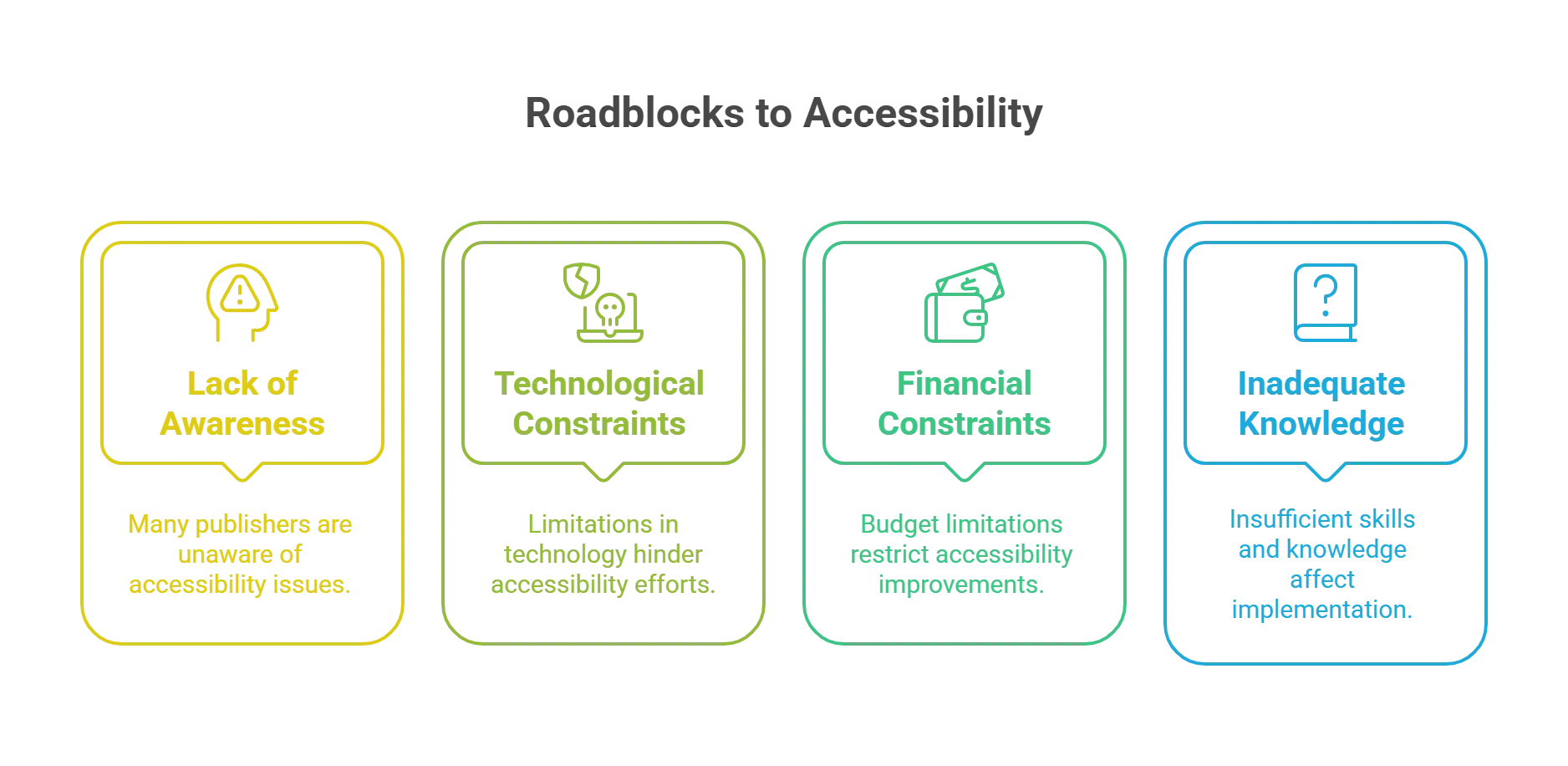
Common Roadblocks to Accessibility in Publishing
The following obstacles can often be expected when considering accessibility in publishing:
1. Lack of Awareness and Understanding
One of the main obstacles to accessibility in publishing is the ignorance of publishers, writers, and designers, among others. Many business experts are unaware of the needs of handicapped readers or the benefits of easily accessible material. This knowledge disparity sometimes results in disregarding accessibility issues while producing the information.
2. Technological Constraints
The fast-changing scene of digital accessibility in publishing presents major difficulties. Many times, publishers battle with antiquated technologies and platforms without accessibility capabilities. Furthermore, technological developments call for ongoing education and adaptation, which can be resource-intensive.
3. Financial Constraints
Creating accessible content can be expensive. Particularly for smaller publishing companies, the demand for specialist software, training, and extra time for testing and changes can tax their budgets. Consequently, often, more immediate corporate demands take precedence over accessibility projects.
4. Inadequate Knowledge and Skills
Many times, publishers have inadequate or no accessibility training at all. Without the appropriate training, publishers and their staff lack the required abilities to apply accessibility features successfully. This disparity can lead to inadequate, easily available content that falls short of impaired readers’ needs.
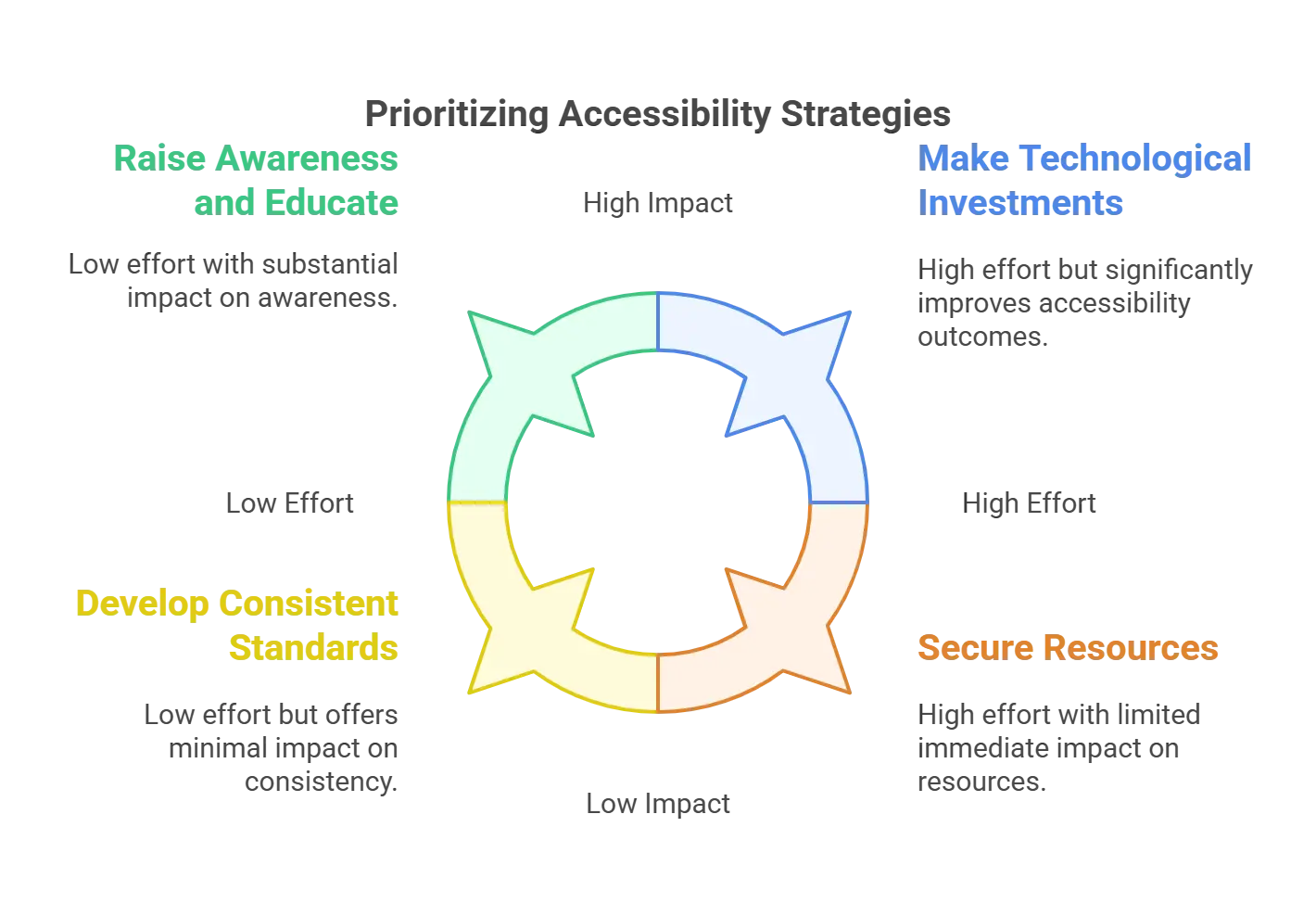
Strategies to Overcome Accessibility Barriers
Here are some inclusive publishing practices you can follow to break down the barriers to accessibility and develop a more inclusive publishing environment:
1. Raise Awareness and Educate
Overcoming accessibility challenges starts with growing knowledge and awareness of accessibility in publishing. Industry conferences, seminars, webinars, and online courses help one accomplish this. The sector may promote a more inclusive attitude by teaching publishers, writers, and designers the value of accessibility and the particular needs of handicapped readers.
2. Make Technological Investments
Publishers should invest in contemporary, easily accessible tools and platforms to solve technological constraints. This includes tools for verifying accessibility features and programs for producing easily accessible formats, such as EPUB3. Maintaining current technological developments can greatly improve digital accessibility in publishing.
3. Secure Resources
Overcoming budgetary limitations requires a lot of strategic planning and funding for access projects. Publishers might look at grants, subsidies, and joint projects with companies that promote accessibility. Furthermore, proving the long-term advantages of easily available materials, such as increasing audience reach and avoiding legal consequences, might help to support the initial outlay.
4. Develop Consistent Standards
Consistency and effectiveness depend on adopting and promoting uniform accessibility regulations in publishing. Industry players—publishers, government agencies, and advocacy groups—should work together to create thorough rules covering all facets of accessibility. This will enable publishers to negotiate the challenging terrain of accessibility criteria more quickly.
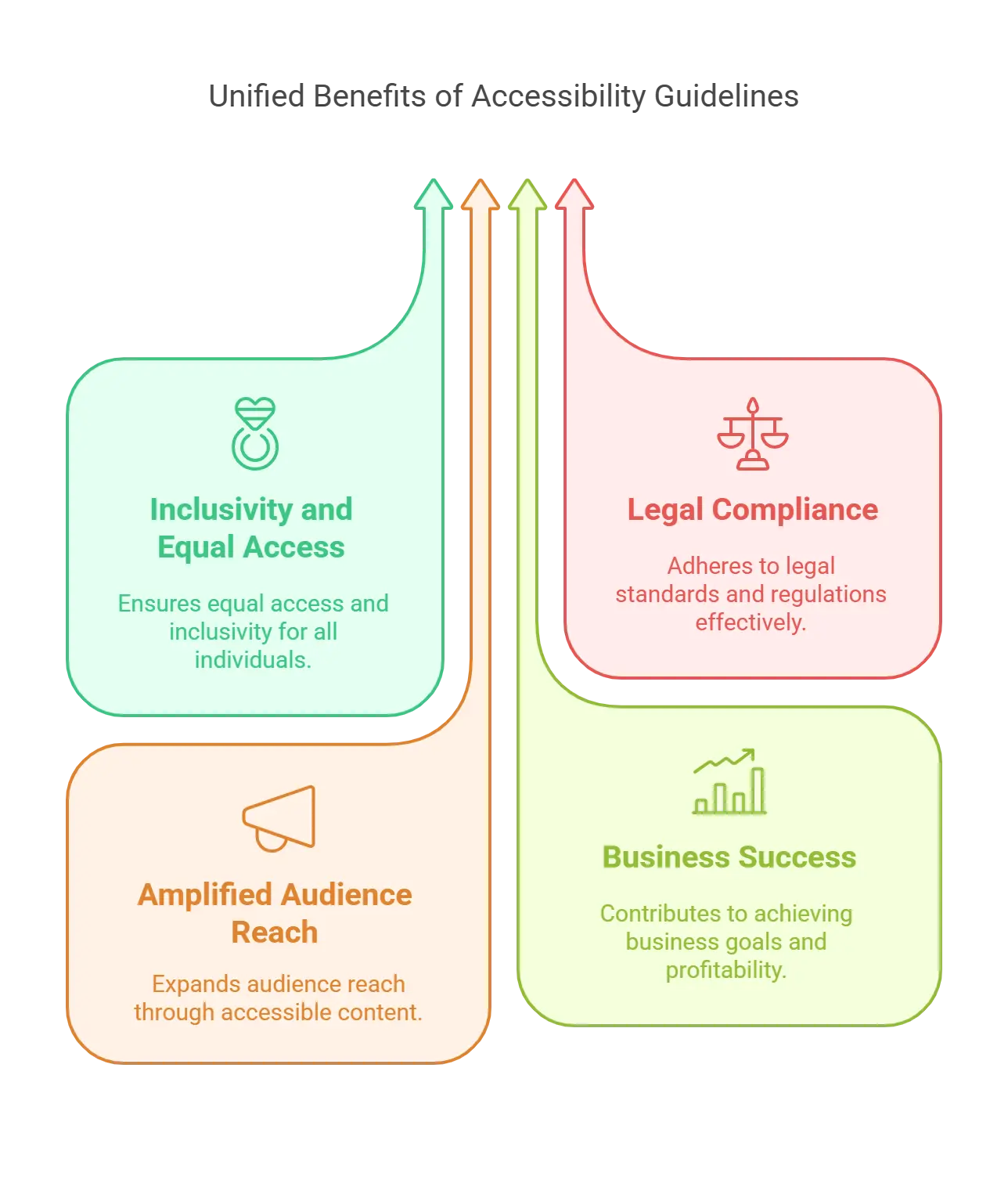
Why Do Accessibility Guidelines for Publishing Matter?
The benefits of digital accessibility in publishing are endless.
Let’s quickly check out why accessibility in publishing has become the need of the hour:
1. Inclusivity and Equal Access For Everyone
At least 2.2 billion people globally have distance vision impairment. And this data is just the tip of the iceberg.
Several other disabilities, such as dyslexia or blindness, can hamper reading experience.
Digital accessibility in publication ensures that individuals with disabilities can interact and engage with content on different platforms.
Accessible publishing removes barriers and provides equal access for individuals with visual motor and cognitive impairments. This ensures universal access to information, from entertainment to educational resources.
For example, several audiobooks help people with blindness consume content in a way that’s comfortable for them.
In addition, inclusive content allows publishers to tap into unexplored markets and reach a broad audience.
2. Ensures Legal Compliance
The European Accessibility Act mandates that a range of products and services, including e-books, be accessible to people with disabilities.
Several countries have followed the EU’s initiative and implemented regulations mandating accessibility guidelines in different areas.
This means non-compliance can result in serious legal consequences, adversely impacting the publishers’ goodwill. Prioritizing accessibility within editorial workflow mitigates legal pitfalls and ensures compliance with WCAG. It also showcases the company’s commitment to inclusive practices.
3. Amplified Audience Reach
One in four adults in the United States lives with some type of disability. This means there’s a relatively untapped market for publishers.
Incorporating digital accessibility practices ensures you can tap into this vast and unexplored market by catering to the needs of 28.7 % of the country.
For example, an ebook compatible with screen readers ensures people with visual or cognitive impairments can access its content. This kind of inclusivity effortlessly addresses the needs of these individuals, thus increasing readership and revenues.
4. Helps You Achieve Business Bottom Lines
An e-book with a magnifier tool provides a hassle-free and convenient reading experience for someone with low vision. This will enhance the overall user experience and increase customer satisfaction. As a result, it allows you to unlock growth opportunities, benefiting your bottom line.
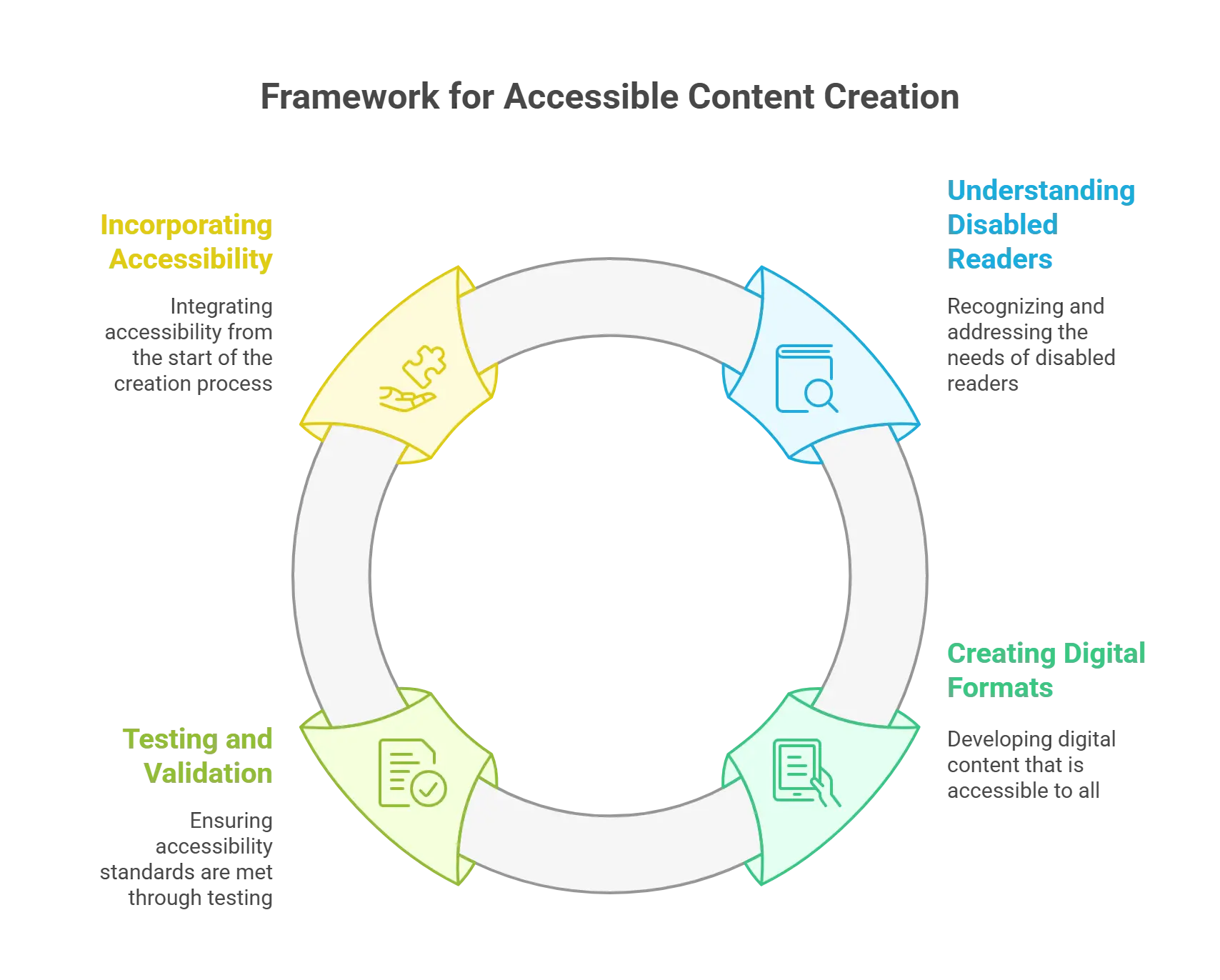
Implementing Accessible Content Creation
For publishers and writers looking to implement pillars of accessibility in their content, consider the following strategies:
1. Understanding the Needs of Disabled Readers
Understanding the several demands of readers with disabilities is the first step in producing accessible content. This covers those with physical, cognitive, visual, and hearing problems, as well as those with visual difficulties. Screen reader compatibility, captioning, simple-to-read layouts, and keyboard navigation are just a few of the accessibility tools each group can call for.
2. Creating Accessible Digital Formats
In publishing, digital accessibility refers to producing material in multiple formats fit for assistive devices. One often-used format with several accessibility characteristics is EPUB3. Publishers should ensure their digital materials have the required accessibility metadata and are correctly structured.
3. Testing and Validation
Testing and validation are critical to ensuring material meets publishing accessibility criteria. These examine accessibility issues using automated tools and hand testing. Incorporating disabled people into the testing process can provide insightful analysis and highlight areas that require improvement.
4. Incorporating Accessibility from the Beginning
From the start of the content creation process, accessibility should be included. This covers thinking about accessibility across the planning, authoring, design, and manufacturing phases. Including accessibility in the process helps publishers prevent expensive and time-consuming retrofits later on.
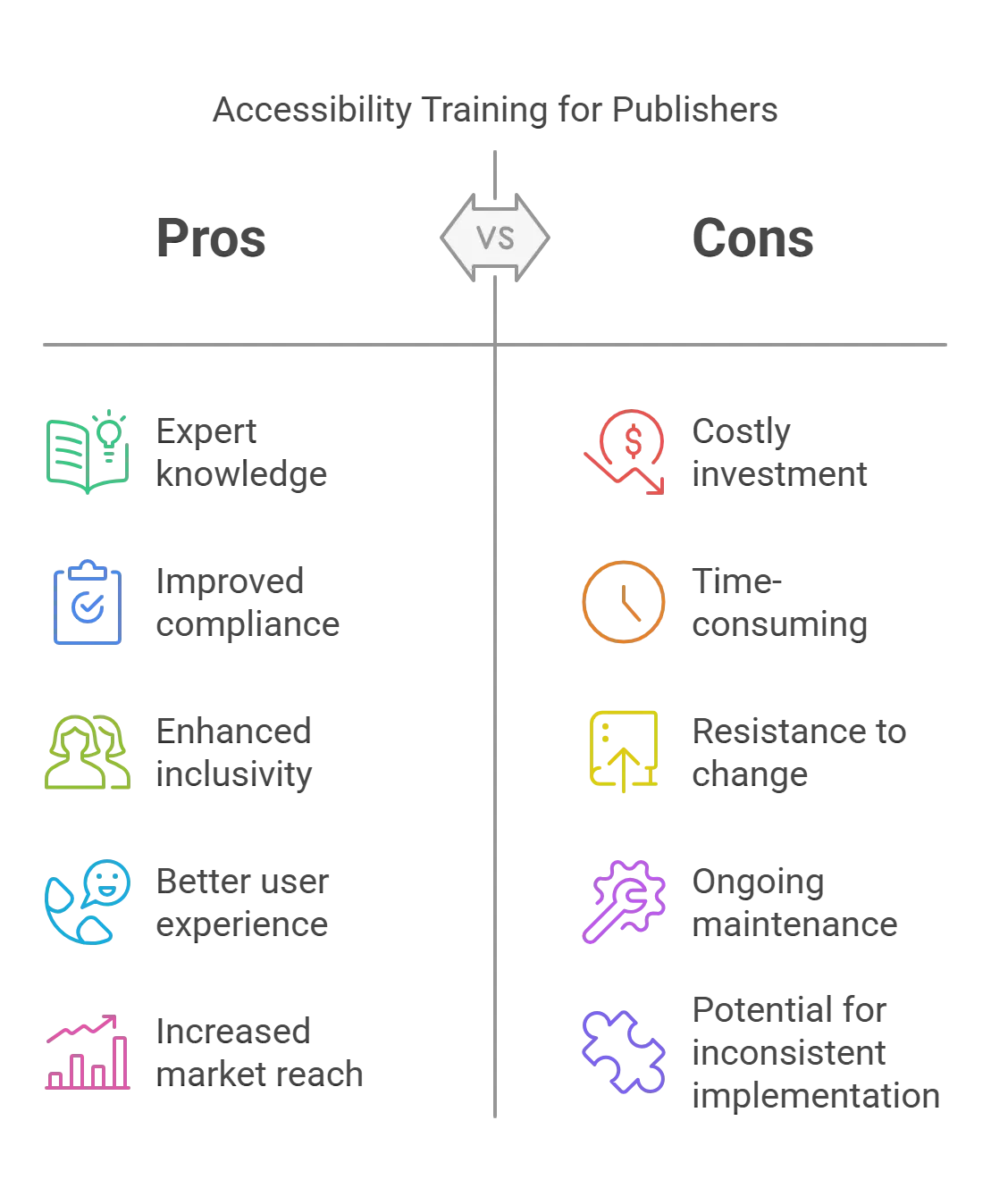
The Value of Accessibility Training for Publishers
Building internal knowledge requires publishers always to be accessible. Training courses should be crafted according to the particular positions in the publishing process, such as those of editors, designers, developers, and authors.
Publishers can assemble a staff capable of producing regularly available materials by developing specific talents.
1. Engaging External Experts
Besides internal training, outside accessibility specialists can offer excellent direction and assistance. These professionals might help with accessibility audits, provide consulting services, and lead training courses. Their specialist understanding will enable publishers to negotiate difficult accessibility issues more successfully.
2. Maintaining New Guidelines
Standards of accessibility and technology are always changing. Publishers must keep updated about the most recent changes to guarantee continuous compliance and efficiency. Frequent training and attendance at industry forums and conferences will enable the team to remain current with the newest best practices and ideas.
On this note, directors of accessibility initiatives within publishing companies should prioritize continuous professional development and encourage their teams to stay informed about the latest advancements and updates in accessibility standards.
Here’s what they can do:
- Regular Training Programs: Organize frequent training sessions and workshops to update staff on the latest accessibility standards and technologies. Internal experts or external consultants can conduct these sessions.
- Accessibility Audits: Conduct regular accessibility audits of published content and digital platforms to identify areas for improvement and ensure compliance with the latest accessibility guidelines.
- Stay Connected with Industry Networks: Encourage team members to join industry forums, attend conferences, and participate in webinars focused on accessibility. Networking with other professionals can provide valuable insights and foster knowledge sharing.
- Access to Resources: Provide access to a repository of up-to-date resources, including guidelines, best practices, tools, and case studies on accessibility. This can be a reference point for employees working on accessible content.
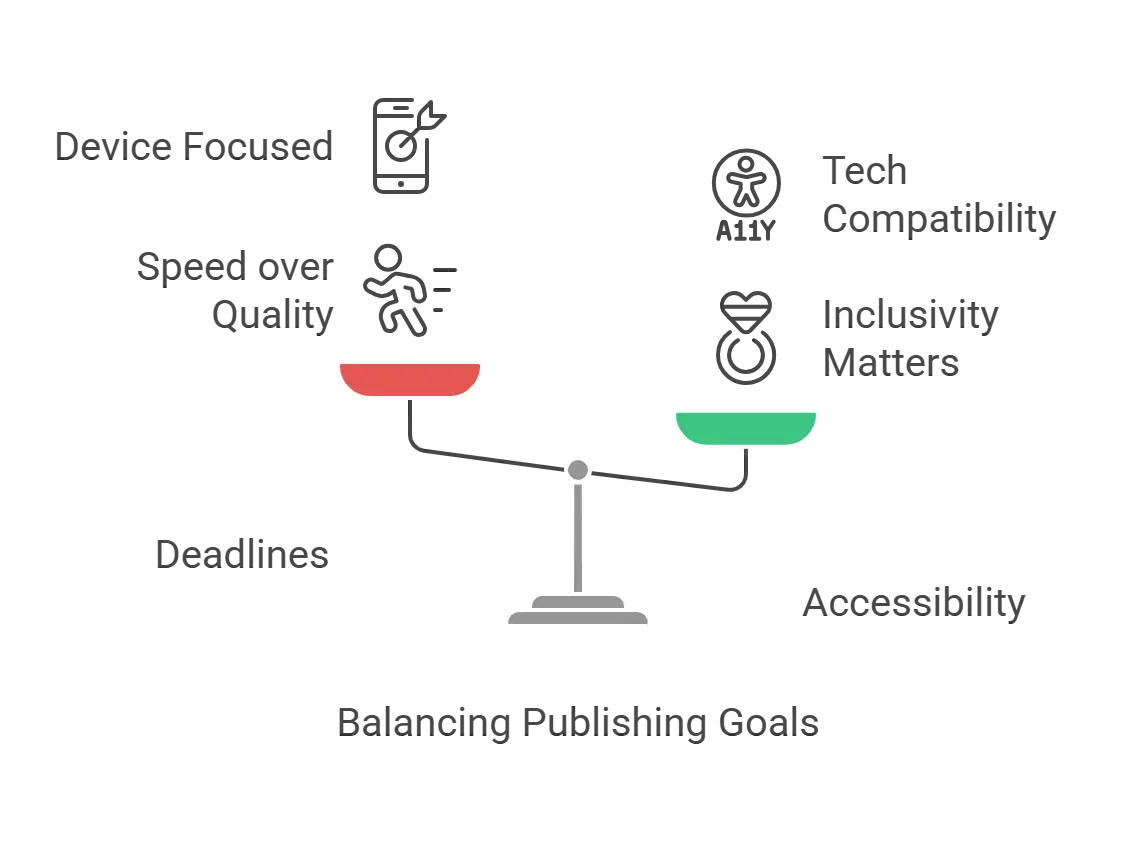
Striking a Balance Between Deadlines and Accessibility in Publishing: Practical Tips for Editorial Managers
Creating a balance between deadlines and accessibility is a double-edged sword. Make one mistake, and be ready to face the consequences.
But what if we say it’s not an impossible feat? You can create accessible content within the deadline by following these simple yet effective strategies:
1. Set Your Priorities Straight
Organizing tasks and setting priorities during the initial phase of the accessibility initiative is no child’s play!
However, once you get there, it will help you integrate accessibility practices into the editorial workflow.
Clear priorities will help you set a realistic deadline, break large tasks into smaller steps, and provide clear goals for each stage. As a result, the editors have enough room to pay attention to accessibility guidelines while making the copies error-free.
2. Take into Account Multi-Device Compatibility
As technology advances and new devices emerge with unique features, it’s crucial to implement digital accessibility. This ensures that content is accessed without any glitches across various devices, from desktops to wearables.
So, while ensuring a seamless editorial workflow, it’s important to consider multi-device adaptability in the account. This ensures the content reaches users regardless of device preferences and disability levels.
3. Compatibility with Assistive Technologies
Remember when Braille script was the only way people with blindness would read? Things have changed drastically since then. Today, digital audiobooks and e-books with screen readers allow people with visual impairments to access information.
Moreover, considering this accessibility requirement, editors can make the content future-proof. This will ensure the content is accessible and usable even when assistive technologies evolve.
4. Future-Proof Content for Evolving Technologies
As we said earlier, technology is advancing at the speed of light. AR, VR, and voice assistants are gaining prominence.
Thus, embracing these emerging technologies in editorial workflow becomes crucial to ensuring enhanced accessibility. This will make your content proof and reduce the need for extensive retrofitting.
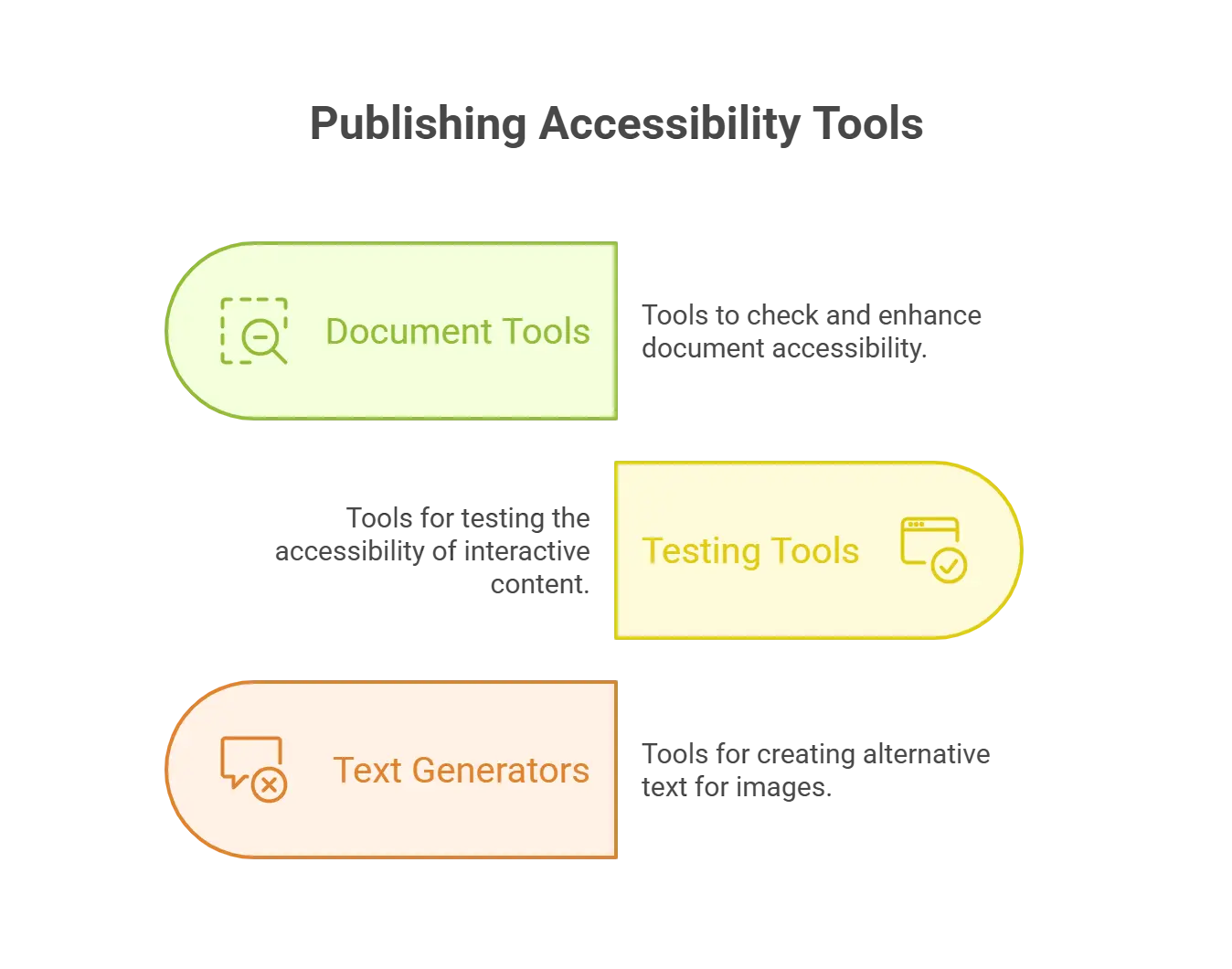
Tools for Ensuring Publishing Accessibility
Below are some essential tools that can help you ensure accessibility in your publishing processes:
1. Document Accessibility Tools
Several publishing accessibility tools ensure the demand for your publication. You can find and fix accessibility problems in your papers with programs like Adobe Acrobat Pro, Microsoft’s Accessibility Checker, and other online validation tools.
Using these technologies, the accessibility auditing procedure may be streamlined, human labor can be decreased, and complete compliance with accessibility requirements can be guaranteed.
2. Interactive Content Testing Tools
Interactive content testing tools assess the accessibility of dynamic and interactive elements such as forms, quizzes, and multimedia. Tools like Accessibility Checker for Forms and Interactive Content Accessibility Tools help ensure these elements are accessible and functional for all users.
Testing interactive content is crucial for providing an inclusive experience across all types of digital interactions.
3. Alternative Text Generators
Alternative text generators, such as automated alt text tools, assist in creating descriptive text for images and multimedia content. Tools like Microsoft Azure’s Computer Vision and Google Cloud Vision API can automatically generate alt text, which can be refined to improve accessibility.
These tools help ensure visual content is accessible to users with visual impairments by providing meaningful descriptions.
By incorporating these tools into your accessibility strategy, you can enhance the inclusivity of your digital content and ensure compliance with accessibility regulations.
Wrapping Up
Compliance with accessibility regulations is important for ensuring your publications remain future-proof. Publishing companies can guarantee that their material is accessible to all by learning and practising standards like Section 508, WCAG, and ADA compliance using the right technologies.
This not only satisfies regulatory demands but also grows your audience and improves the inclusive reputation of your company. A more inclusive publishing business and greater dedication to accessibility may be achieved by appreciating accessibility rather than just adhering to regulations.
At Hurix Digital, we specialize in helping you implement a robust accessibility strategy tailored to your publishing needs. With our expertise and innovative solutions, we ensure that your content is both compliant and inclusive.
Sounds interesting? Book an appointment with us!

Vice President – Digital Content Transformation. He is PMP, CSM, and CPACC certified and has 20+ years of experience in Project Management, Delivery Management, and managing the Offshore Development Centre (ODC).








