
Mobile App Accessibility Testing Made Easy! The Only Guide You Need
In today’s modern world, mobile devices have become an essential part of daily life for millions of people. In 2022, over 60% of the global internet population used smartphones to connect to the web.
With mobile technology (AI and ML) being more affordable and available than ever, smartphones have evolved into important information, communication, and entertainment tools. As per a CDC report, up to 1 in 4 (27%) adults in the U.S. have some form of disability. Using a mobile with a physical disability can be a frustrating experience.
As mobile ownership and internet usage continue to grow, it’s highly essential to ensure that web-enabled devices are accessible to everyone, including users with disabilities. Here’s when mobile app accessibility testing comes in.
This checklist, which we created in this article, will become your go-to resource for creating inclusive digital experiences for all. It is comprehensive and covers all the crucial aspects of accessibility testing so that you can develop and optimize your mobile apps and websites for maximum reach and impact.
Table of Contents:
- Understanding Mobile App Accessibility Testing
- Benefits of Mobile Accessibility
- Four Common Pitfalls in Mobile App Accessibility Testing
- Three Solutions to Avoid Issues in Mobile App Accessibility Testing
- The Ultimate Checklist to Follow For Mobile App and Web Accessibility
- Wrapping Up
Understanding Mobile App Accessibility Testing
Mobile app accessibility testing is the process of evaluating the usability of an application or website for people with disabilities. These include users who are blind or have low vision, limited mobility, or hearing loss.
Users with varying abilities use assistive technologies like screen magnifiers, screen readers, and voice recognition software to access digital information and functionality. The ultimate goal of accessibility testing is to ensure that these individuals can access and interact with digital content without difficulties or barriers.
Mobile app accessibility testing can be automated using AI and machine learning-driven tools that simulate assistive technologies. It can also be performed manually by having differently-abled users evaluate the website or application.
Artificial Intelligence in quality assurance offers the ability to self-learn and test applications without human intervention. Accessibility testing has become an indispensable part of software development as it ensures that digital content is accessible to the widest possible audience.
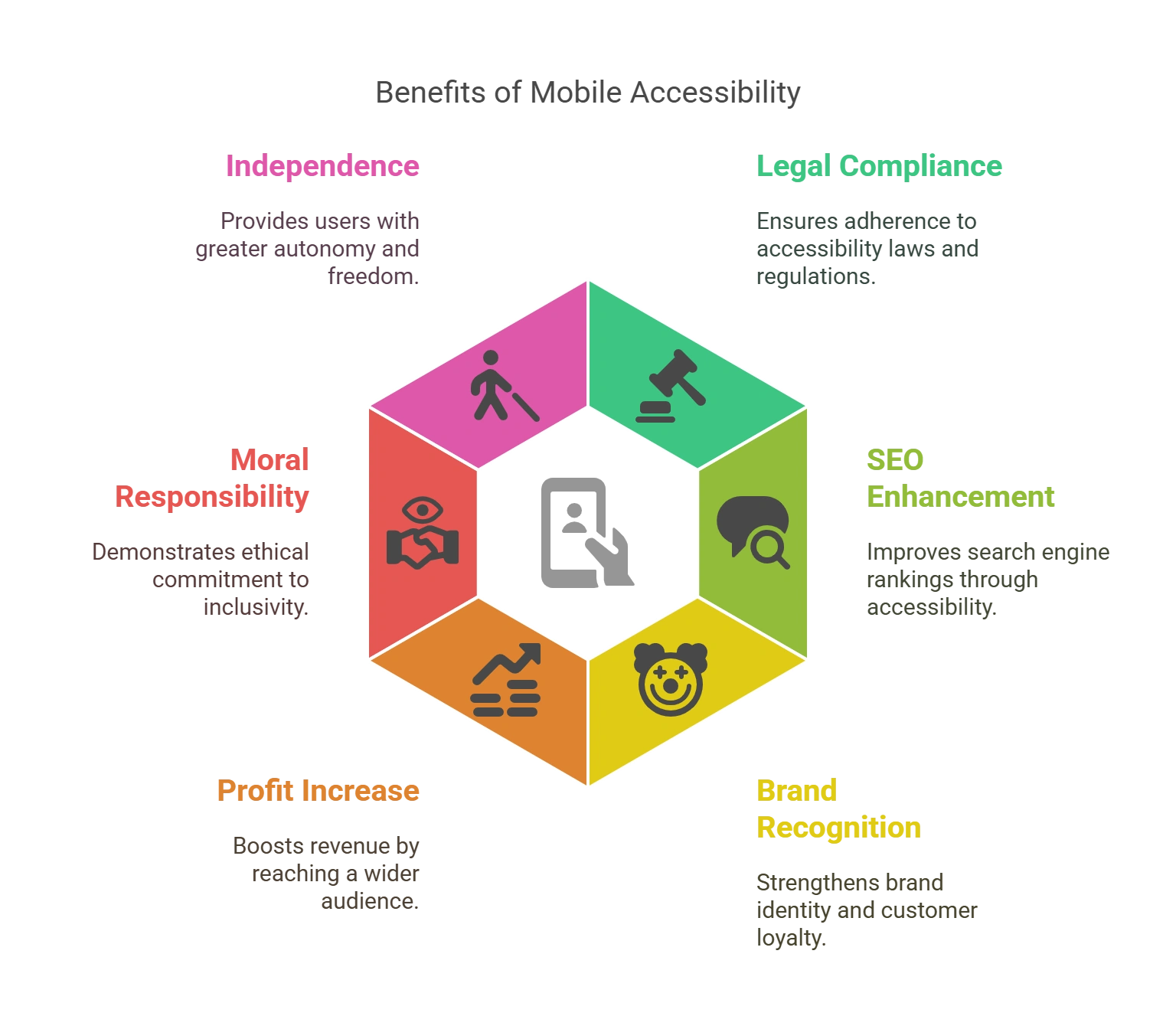
Benefits of Mobile Accessibility
Having mobile-accessible applications and websites is very important and beneficial as well, in the following ways:
1. Upholds Your Legal Responsibility
With the use of smartphones and the internet on the rise, digital accessibility has become a civil right for people with disabilities. In this scenario, ensuring mobile app accessibility can save you from legal issues, such as lawsuits filed for discrimination. It also helps you adhere to the three laws and guidelines:
- Section 508: A US law that requires federal and associated companies to make technology and electronic data accessible to everyone, including people with disabilities.
- ADA: The Americans with Disabilities Act mandates businesses to make electronic content accessible to people with disabilities.
- WCAG: Web Content Accessibility Guidelines are a standard set of guidelines explaining how to make your electronic content accessible to everyone.
2. Enhances SEO
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) aims to bring traffic to your website and mobile applications by improving your ranking in search engines like Google. Along with expanding your reach, higher visibility increases the number of conversions.
Mobile accessibility enhances your SEO by making your content easy to find. It also makes your mobile applications user-friendly and improves their navigability.
Easy-to-navigate applications and websites decrease the bounce rate, i.e., the percentage of visitors who leave your site after viewing only one page.
3. Builds Brand Recognition and Customer Retention
Ensuring mobile accessibility showcases that you have a law-abiding business that is mindful of its customers and their requirements. Being inclusive of every single customer creates a reputable image for your brand.
Developing a diverse culture attracts partners for collaboration, thereby establishing a good reputation for your brand in the industry.
Fostering inclusivity increases the access of people with disabilities to quality customer services. Providing good customer service increases customer satisfaction, which causes them to subscribe to your business and thus results in their retention.
4. Increases Your Profits
Mobile accessibility equips your mobile applications with content that can be viewed in different ways, including videos, audio, alt-text, and written transcripts.
This makes your content accessible to people who are experiencing age-related decline, are not fluent in English, are suffering from injuries, etc.
Thus, mobile accessibility enables you to reach a broader customer base with your services and products. This, in turn, improves your likelihood of increasing your sales and profits.
5. Upholds Your Moral Responsibility
People with disabilities are an equal part of society, making accessible mobile applications and websites a moral responsibility of enterprises worldwide.
When done in a collaborative environment, creating mobile-accessible products results in the contribution of every company employee to a noble cause.
For example, a designer can work on the application’s design elements and ensure that they are appropriate for all users, a developer can develop the language for the application, etc.
6. Offers a Great Degree of Independence
Mobile accessibility provides an opportunity for becoming independent to people who live with disabilities. With just a few taps, swipes, and voice commands, they can do things such as:
- Buy groceries and gifts
- Handle banking and finances
- Take an online course
- Purchase airplane tickets
- View event calendars
- Keep in touch with the current news
- Book a cab
Mobile app accessibility testing encourages people with disabilities to participate in activities outside their homes. It makes them self-sufficient, supports active aging, and reduces the cost of senior care services. The reduced demand for special services brings economic benefits to the entire society.
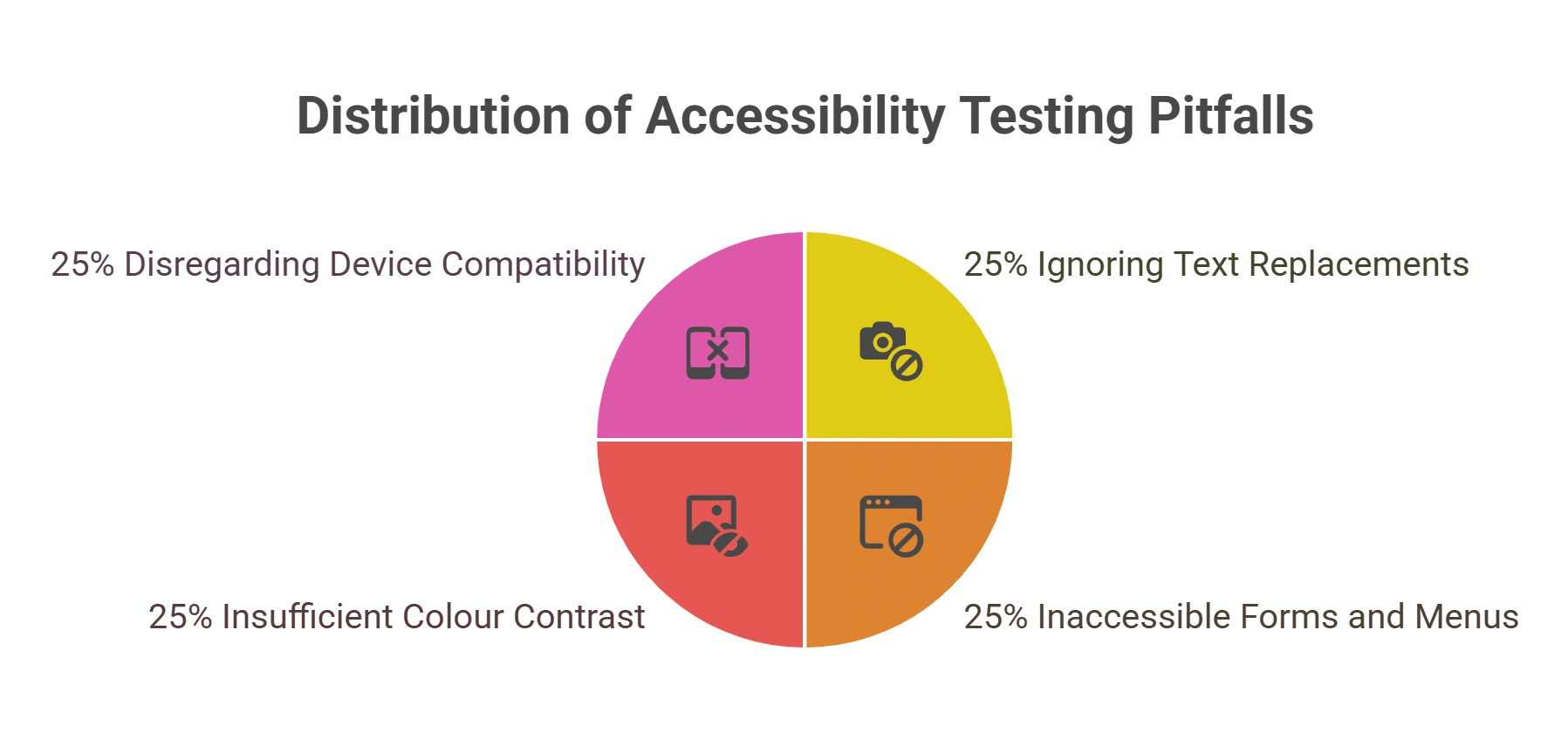
Four Common Pitfalls in Mobile App Accessibility Testing
Mobile app accessible testing is an essential process that significantly improves the application’s ability to comply with legal requirements and avert possible legal action. Here are some of the common pitfalls that need to be addressed in the process:
1. Ignoring Text Replacements for Pictures
It is imperative to tackle the problem of neglecting text alternatives for images in accessibility testing. This indicates that pictures in digital content do not have “alt text” or descriptive text, which is necessary for screen readers or people with visual impairments.
An image’s alt text describes its content and intended use through text. This data shows that individuals with visual impairments can comprehend and interact with the content. If alt text is not done correctly, people who use screen readers or have sluggish internet connections could lose out on important information.
To guarantee universal digital accessibility, testers and testing service providers need to ensure that descriptive alt text is present.
2. Establishing Inaccessible Forms and Menus
A critical component of mobile app accessibility testing is evaluating the look and feel of interactive features on applications, such as forms and menus. People with disabilities might not be able to navigate or use these elements or key features.
Menus should be designed to work with various input devices, including screen readers, spoken instructions, and keyboard navigation. They should also make it simple for all users to interact with them by offering labels, feedback, and clear guidelines.
Finding and fixing the existence of inaccessible forms and menus is crucial for accessibility.
3. Not Providing Enough Colour Contrast
When it comes to mobile app accessibility testing, it’s critical to focus on the problem of adequate color contrast. This is when the background and text color selections don’t adhere to the required color contrast guidelines.
Sufficient color contrast is imperative for those with low vision, color blindness, or other visual impairments. It ensures content that is readable and understandable. For visual accessibility, text and images must have a minimum contrast ratio of 4.5:1, with larger text needing a ratio of 3:1.
Finding situations in which there is insufficient color contrast is crucial for accessibility testing. When testing digital platforms, testers should make sure that text and other visual components adhere to contrast specifications.
4. Disregarding Mobile Device Compatibility
Accessing digital content is most prevalent with mobile devices. Hence, it is vital to guarantee that applications on mobile devices are usable by everyone, including those with disabilities.
A disjointed user experience may result from accessibility testing that disregards mobile device compatibility. This is due to the possibility that features designed for desktop computers may not perform well on devices with smaller screens or touch-based interfaces.
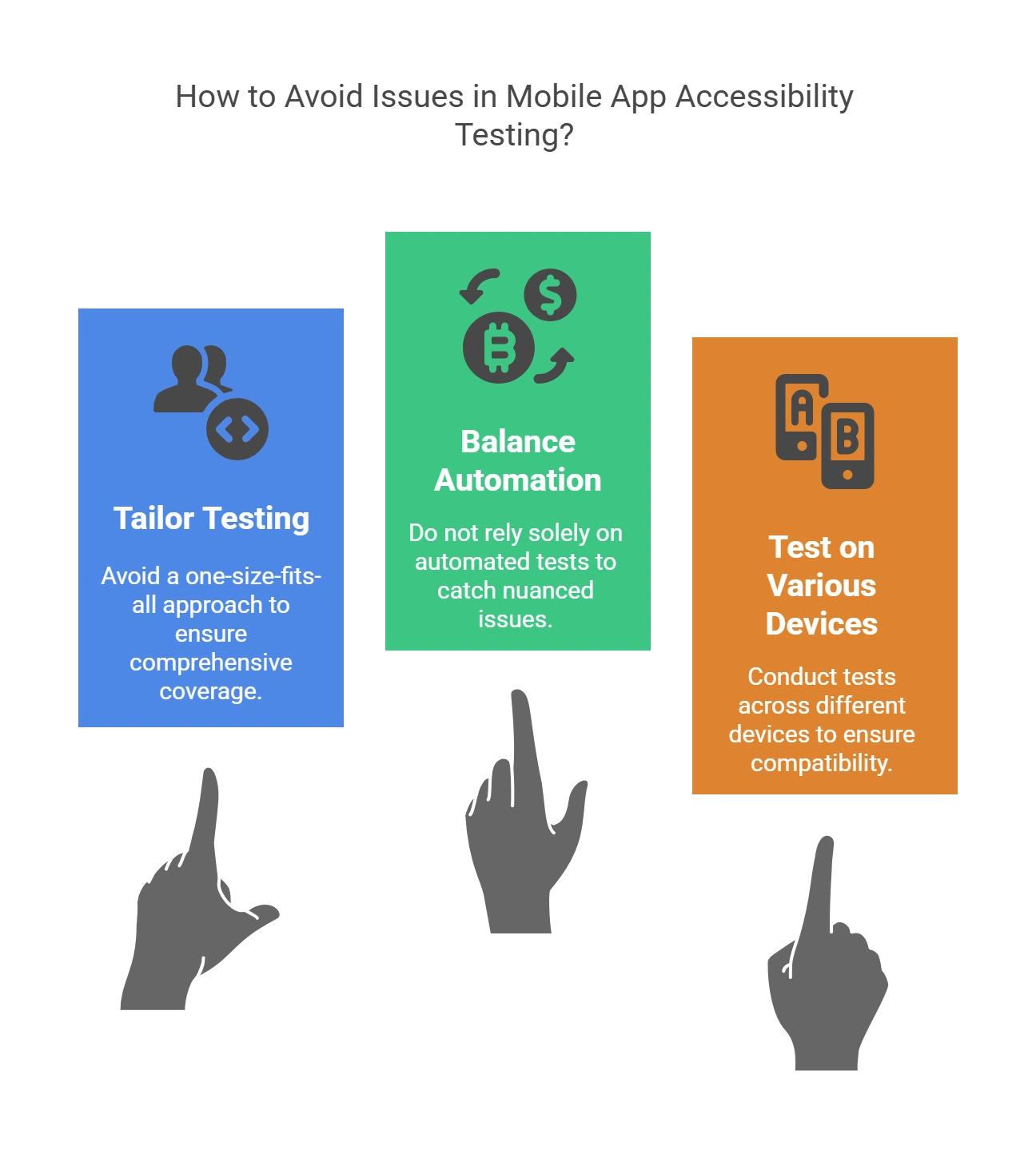
Three Solutions to Avoid Issues in Mobile App Accessibility Testing
A large number of the most widely used apps on Android and iOS have substantial accessibility issues. Adopting accessibility can help you better serve all users and highlight the values of your brand.
Here are some effective tips to do so:
1. Avoid Applying a One-Size-Fits-All Strategy to Mobile Testing
Each application is unique, and testing a web application differs greatly from testing a native application. The particular features of an application might call for extra thought.
If you’re creating an app for art, for instance, you might need to include communications that restrict accessibility. Nevertheless, you can still increase accessibility by adhering to other pertinent WCAG criteria.
2. Do Not Rely on Automated Tests Entirely
For iOS and Android, automated accessibility tools are available. But no automated test is flawless, and there aren’t many tools available for testing mobile apps.
An automated tool might overlook certain barriers unique to a given mobile context. Automated tools are also usually limited to specific kinds of content; for example, while automation can identify most of the obstacles in a web application, it might overlook dozens of critical problems in a native application (or vice versa).
It’s also critical to keep in mind that certain WCAG requirements call for human judgment.
3. Conduct Tests Using Various Devices
Though it might seem apparent, not every user is using the most recent iPhone. If your app is a hit, your user base will be sizable and comprise a range of gadgets and assistive technologies.
Your mobile app testing approach should represent the whole range of your user base. To achieve this, test your product as much as you can.
- Use on-the-go screen readers to check your formatting
- Make sure your app is keyboard accessible by testing it using a keyboard instead of touchscreen controls
- Use real devices everywhere possible. Simulators of mobile environments are not flawless, particularly if your application relies on accelerometers, geolocation, or other characteristics unique to mobile devices.
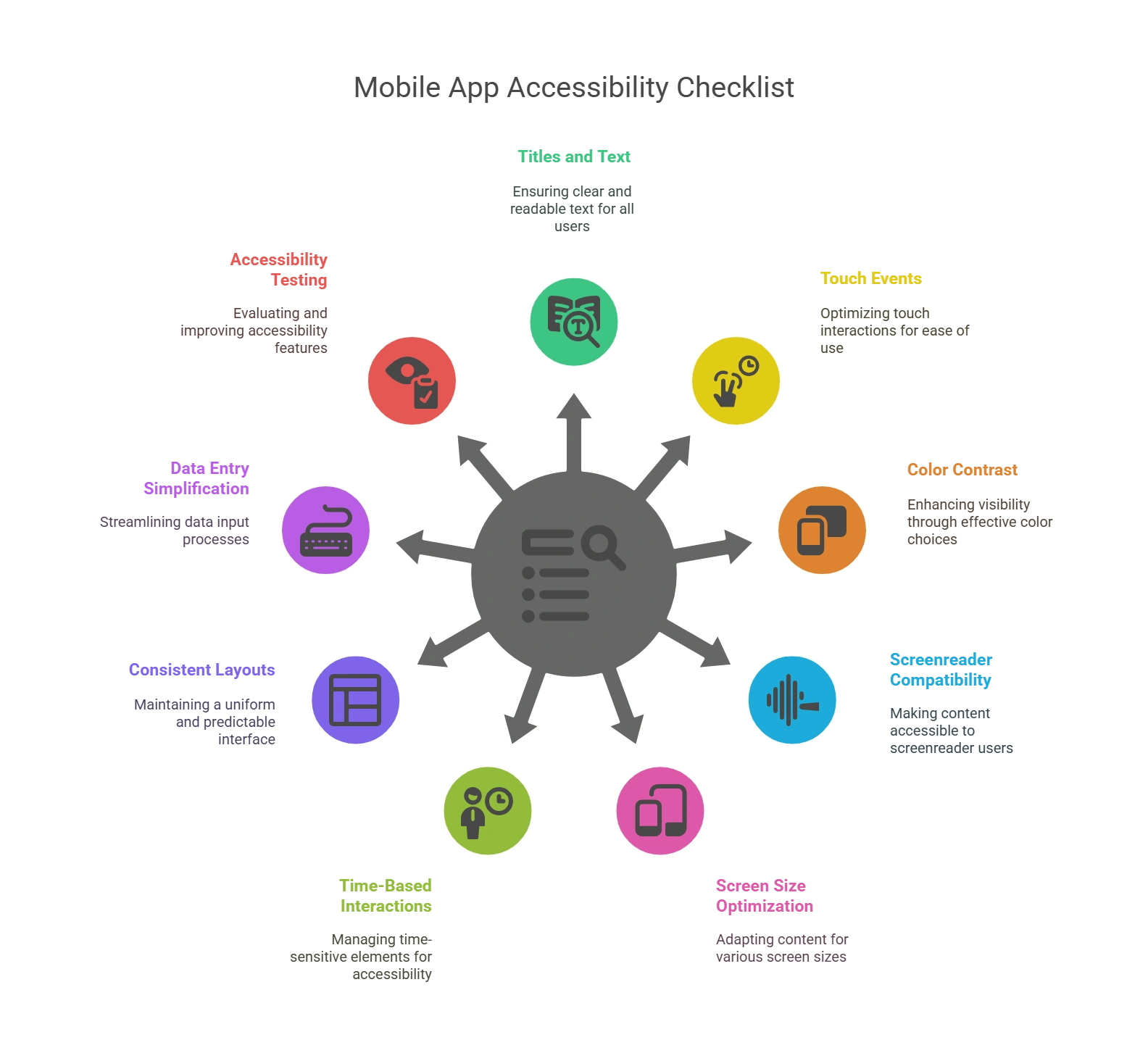
The Ultimate Checklist to Follow For Mobile App and Web Accessibility
Once you take care of these parameters on your mobile app, it will automatically become accessible.
1. Titles and Text
- Make sure your app has a title.
- Implement an ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) in HTML. This will show the structure of the app or a page and mention roles or properties on the app, like search, navigation, banners, etc.
- Maintain hierarchy in the headings.
- Choose easily readable fonts and make the text size adjustable.
2. Touch Events
- Don’t use the touch-down event for any activity.
- If the up-touch starts an action, offer the choice to stop or undo it.
- It can also have the option to reverse any event due to the down action right after such an unwanted event has occurred.
- Keep the touch targets like buttons and links large enough (minimum 9 mm height and width each) for the users to avoid accidentally touching something else.
- The interactive elements should be placed so anyone can access them (the same for left and right-handers, for example). For example, buttons could be at the center.
- You can also add accessibility options to use the app. For example, there are hands-free technologies now where users can interact using audio. Or you can allow users to navigate through the keyboard or other external devices.
3. Color Contrast
- Use sufficient color contrast between the foreground (think text) and background, as well as for interactive elements, to accommodate users with low vision or color blindness.
- Keep the foreground-to-background color contrast ratio at 4.5:1 for standard text and 3:1 for large text and icons.
- When the contrast ratio is low, it becomes difficult for specially-abled users to read.
4. Screenreader Compatibility
- Test your app with popular screen readers for visually impaired individuals, such as VoiceOver (iOS) and TalkBack (Android).
- You can ensure all elements are correctly labeled and the content is read in the correct order. If not, you can make changes.
5. Screen Size Optimization
- Offer preset screen sizes designed specifically for users to choose from, allowing them to get the maximum out of the screen and not lose out on features because of zooming in.
- You can also reduce the amount of data present on each app page.
- Change the link text size according to the width of the app view.
6. Checking Time-Based Interactions
- Any app interactions should not be time-based to accommodate the needs of everyone.
- Instead, offer them the option to extend time if such interactions are necessary.
7. Consistent Layouts and Navigation
Maintaining consistent navigation throughout the app will help users familiarize themselves with the interface and predict where elements will be located.
It can overwhelm many to readjust themselves to new layouts and constantly adapt.
8. Simplifying Data Entry
- Allow users to enter data using methods other than text, like speech or multiple-choice questions.
- Information that can be auto-entered, like dates, can also help make the app more accessible.
- Using tools like auto-correct and autofill also goes a long way.
9. Test to Scale Up Your Accessibility
The most important part is to test your app with specially-abled individuals and get feedback from real people.
Wrapping Up
Although the above checklist is not exhaustive, it covers key components of mobile app accessibility testing. You can also leverage AI machine learning-driven tools to identify accessibility issues and ensure the mobile app or website is completely accessible to everyone.
Integrating accessibility testing into the mobile application development process can increase customer satisfaction, increase app usage, nurture inclusivity, and comply with all accessibility-related legal mandates.
Need help with mobile app accessibility testing or AI in quality assurance? Hurix Digital can be your digital transformation partner. Our team of top-level IAAP-certified professionals has years of experience delivering best-in-class accessibility testing services for mobile apps, e-learning platforms, and more.
Get in touch with us to know more!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What disabilities should mobile testing address?
A1: Visual, auditory, cognitive, and motor impairments must all be considered during testing.
Q2: Which screen readers work for mobile testing?
A2: VoiceOver for iOS and TalkBack for Android are the primary tools used.
Q3: How do gestures impact accessibility?
A3: Non-standard gestures may confuse users—always provide alternative controls and voice actions.
Q4: Can overlays ensure mobile compliance?
A4: No—native app accessibility must be built in, not added as a layer.
Q5: What is the best way to test real usage?
A5: Combine emulators with manual testing by people with disabilities.

Vice President – Content Transformation at HurixDigital, based in Chennai. With nearly 20 years in digital content, he leads large-scale transformation and accessibility initiatives. A frequent presenter (e.g., London Book Fair 2025), Gokulnath drives AI-powered publishing solutions and inclusive content strategies for global clients








