
A Beginner’s Guide to UI and UX: What You Need to Know
Summarize with:
In 2026, user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design are essential for creating digital products that not only look great but also drive engagement and retention. Modern design focuses on accessibility, data‑driven insights, micro-interactions, and seamless cross‑device experiences that delight users and elevate business outcomes.
Whether you’re designing a website, mobile app, or enterprise platform, mastering UI UX design principles is vital to stand out in the competitive landscape. This in-depth guide will equip you with an understanding of core concepts, actionable best practices, and the latest trends shaping the field. Explore the foundations of UI UX design and learn how to transform ideas into impactful user experiences.
Table of Contents:
- What is UI Design?
- What is UX Design?
- Are UI & UX The Same?
- Comparison Table: UI vs. UX
- What Are the Principles of User Interface Design?
- What Are the Principles of User Experience Design?
- UI/UX Tools and Resources for Beginners
- The Website Development Process: A 4-Stage Approach
- Modern Trends Shaping UI UX Design
- 7 Common UI/UX Mistakes Beginners Make
- What is the Difference Between UI & UX?
- FAQS
What is UI Design?
UI stands for “User Interface.” It refers to how a user interacts with a software application or a digital device. The user interface can include various elements such as buttons, menus, text boxes, and graphical representations that allow the user to control and interact with the software or device.
A good user interface is designed to be intuitive, easy to navigate, and efficient. It should help the user accomplish their goals quickly and without confusion. UI design is an important aspect of software and digital device development as it directly affects the user experience and can impact the adoption and success of the product.
What is UX Design?
UX stands for “User Experience.” It refers to the overall experience that a user has with a product, such as a software application, website, or digital device. UX design involves understanding the needs, goals, and behaviors of users, and then designing a product that meets those needs in a way that is easy and enjoyable to use.
UX design involves several different disciplines, including user research, interaction design, information architecture, usability testing, and visual design. The goal of UX design is to create a product that is both useful and delightful to use, and that meets the needs and expectations of its users.
A good user experience is crucial for a product’s success, as it can directly impact key factors such as user adoption, customer satisfaction, and engagement. UX design is an iterative process that involves continuous testing and refinement to create a product that meets the needs of its users and provides a positive overall experience.
Are UI & UX the Same?
UI (User Interface) and UX (User Experience) are not the same, but they are closely related concepts. UI refers to the visual design and interactive elements of a product, while UX refers to the overall experience a user has with the product. While these two concepts are closely related and often work together, they are not the same thing.
UI refers to the visual design and interactive elements of a software application or digital device that enable users to interact with it. This includes everything from the layout of the user interface to the typography, color scheme, icons, buttons, and other visual elements. The goal of UI design is to make the user interface easy to use, visually appealing, and intuitive.
UX, on the other hand, is a broader term that encompasses the entire experience a user has with a product, including their emotional response to it. This includes how easy it is to learn and use the product, how enjoyable it is to use, and how well it meets the user’s needs and expectations. UX design considers factors such as user research, user testing, and the overall user journey to create a product that is both useful and enjoyable to use.
Comparison Table: UI vs. UX
| Aspect | UI (User Interface) Design | UX (User Experience) Design |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Visual elements and interactive components | Overall user journey and satisfaction |
| Key Question | How does it look and feel? | Is it easy, intuitive, and enjoyable to use? |
| Components | Buttons, icons, typography, color schemes, layout, microinteractions | User research, personas, journey maps, wireframes, prototyping, usability testing |
| Goal | Create an aesthetically pleasing and functional interface | Ensure the product meets user needs and provides a seamless experience |
| Process | Design mockups, prototypes, style guides, visual consistency | Research, testing, iterative improvements, analytics-driven design |
| Tools | Figma, Adobe XD, Sketch, Canva | Maze, Hotjar, Google Analytics, UsabilityHub |
| Measurement | Visual consistency, responsiveness, accessibility compliance | Task completion rate, user satisfaction, engagement, retention |
What Are the Principles of User Interface Design?
The principles of UI design are a set of guidelines that designers follow to create user interfaces that are visually appealing, easy to use, and effective at achieving their intended goals. Here are some of the key principles of UI design:
- Keep it simple: A simple and intuitive user interface is easier for users to understand and navigate. Avoid cluttered designs and unnecessary elements that can distract users from their goals.
- Be consistent: Consistency in design, layout, and typography helps to create a predictable user experience, which makes it easier for users to learn and use the interface.
- Use clear and concise language: Use language that is easy to understand and avoid technical jargon. Use clear labels and instructions to guide users through the interface.
- Provide feedback: Feedback helps users to understand the consequences of their actions and provides a sense of control over the interface. Provide visual feedback, such as animations or sound effects, when users interact with elements on the screen.
- Use visual hierarchy: Use visual elements such as color, size, and contrast to create a clear visual hierarchy that guides users through the interface and highlights important elements.
- Provide easy navigation: Provide clear and easy-to-use navigation that allows users to move through the interface quickly and efficiently.
- Design for accessibility: Ensure that the user interface is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. Use design techniques such as contrast, font size, and screen reader compatibility to make the interface accessible to everyone.
- Mobile‑First & Responsive Design: Ensure layouts adapt fluidly across screen sizes and devices.
- Microinteractions: Use subtle animation or feedback to acknowledge user actions and make interaction feel more human.
These principles provide a useful framework for designers to create effective user interfaces that meet the needs of their users.
What Are the Principles of User Experience Design?
Here are some general guidelines for UX design:
- Conduct user research: Before designing a product, it’s essential to understand the users who will be using it. Conduct user research to gain insights into their needs, goals, and behaviors.
- Create personas: Personas are fictional representations of the target users. Create personas to better understand their motivations, goals, and pain points.
- Map out the user journey: Map out the user journey to understand the flow of the user’s experience with the product, from start to finish. This helps to identify pain points and opportunities for improvement.
- Design for mobile devices: With the rise of mobile devices, it’s essential to design for smaller screens and different user behaviors.
- Use prototyping: Use prototyping to quickly iterate on design ideas and test them with users.
- Use white space: White space is essential for creating a clean and uncluttered design. Use it to highlight important elements and create a more balanced layout.
- Use clear and simple language: Use clear and simple language in the product to make it easier for users to understand and use.
- Consider accessibility: Design the product to be accessible to everyone, including users with disabilities. Consider factors such as contrast, font size, and screen reader compatibility.
- Test and Iterate: UX design is an iterative process. Test the product with users and use their feedback to improve the design.
- Accessibility & Inclusive Design: Consider cognitive, motor, and sensory needs when crafting experiences.
- A/B Testing & Data‑Driven Improvement: Use analytics, A/B testing, and heatmaps to validate design decisions and improve outcomes over time.
The specifics of UX design will vary depending on the product, the users, and the design goals, but these guidelines offer a solid starting point.
UI/UX Tools and Resources for Beginners
For beginners diving into UI and UX design, the right tools can make learning and practice much easier.
Popular design platforms like Figma, Adobe XD, and Sketch help you create interactive prototypes and layouts, while usability testing tools such as Maze, Hotjar, and Google Analytics provide insights into user behavior. Combining these tools with online tutorials, design communities, and case studies will give you a strong foundation to start building engaging and user-friendly digital experiences.
• Figma: Cloud‑based collaborative design and prototyping platform.
• Adobe XD: Used for creating interactive prototypes.
• Sketch: Popular UI design tool (Mac only).
• User Testing Tools: Platforms like Hotjar, Maze, or Google Analytics for usability feedback.
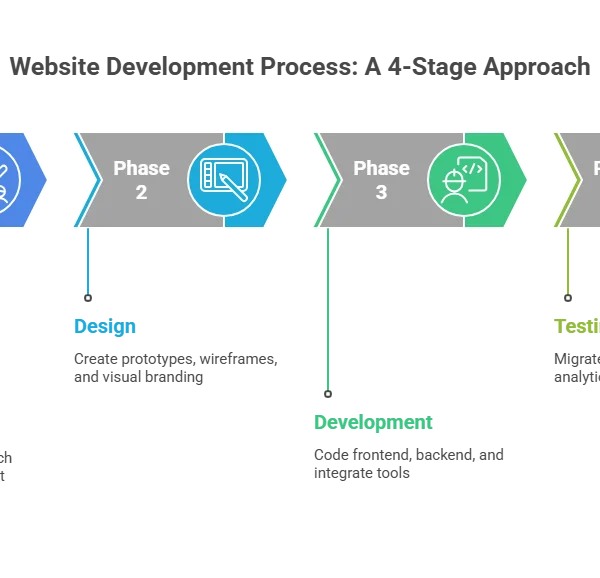
The Website Development Process: A 4-Stage Approach
Creating a successful website involves a structured process. A documented, standardized series of actions helps coordinate teammates, stakeholders, and resources to ensure every aspect of the project is handled and completed on schedule. This website development process can be broken down into four crucial stages.
Phase 1: The Initial Phase of Planning
A solid plan is the foundation of any website. This strategy helps identify the site’s objectives, target audience, features, and overall layout.
- Establish user/business objectives: Define the primary purpose of the website. Is it to provide information, generate leads, facilitate sales, or something else?
- Perform user research: Create personas, conduct interviews, and gather data to understand your target market.
- Identify the needs: Determine the features, sections, and integrations required to meet the website’s goals.
- Lay out the content and design: Develop flowcharts, sitemaps, and content strategies based on priority.
In Phase 1: Include UI/UX research outputs like personas and journey maps as documented assets.
Phase 2: Designing the Website
Once the plan is in place, the design phase begins. This involves creating a website prototype and deciding on the general style and user experience.
- Focus on visual branding: Use color palettes, typefaces, and images that align with your brand identity.
- Create prototypes and wireframes: Develop low-fidelity outlines or high-resolution visual comps to map out the design.
- Design foundational pages: Create designs for the homepage, content pages, and other key templates.
- Improve user experience flows: Ensure that navigating through web pages is simple and intuitive.
Phase 3: Development
With approved designs, the development team starts coding the frontend and backend frameworks. This intricate stage requires creative technology, modern web development methods, and analytical skills to build a fast, functional website.
- Program site design: Set up the content management system and hosting platforms.
- Integrate external tools: Link APIs, extensions, and payment gateways as planned.
- Frontend development: Build the user-facing part of the site using HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and libraries like Angular or React.
- Backend construction: Develop the server-side logic using languages such as Python, Ruby, or PHP.
- Database organization: Create efficient data structures.
- Establish an admin interface: Allow clients to manage content easily.
Phase 4: Testing and Launching
After development, the website undergoes rigorous testing to ensure everything functions correctly. This phase includes functional testing and user acceptance testing.
- Content migration: Move all pages, blog posts, and products to the new site.
- Data analysis configuration: Link tools like Google Analytics and Tag Manager.
- SEO setup: Verify that every page has optimized metadata.
- Security: Install firewalls and anti-malware software.
- Soft launch: Release the site to a limited audience to gather early feedback.
- Official launch: Announce the website to the public, often with promotional activities.
- Post-launch tracking: Monitor performance and address any critical issues.
Include usability testing sessions, task completion rates, and heatmaps to validate UX decisions before full launch.
Modern Trends Shaping UI UX Design
The field of website development is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting user expectations. Staying current with these trends is vital for creating engaging and effective digital experiences.
1. Voice Interfaces and Voice Search Optimization
Modern UI UX design increasingly incorporates voice commands alongside traditional inputs. This requires optimizing websites for voice recognition technology and ensuring compatibility with various voice-enabled devices. The rise of voice-activated search means developers must focus on natural language processing to deliver seamless user interactions.
2. AI-Powered Web Development and Personalization
Artificial Intelligence is transforming how websites are built and experienced. AI-powered tools can automate tasks from generating domain names to optimizing images, allowing developers to focus on innovation. Furthermore, AI and machine learning algorithms enable deep personalization, tailoring content and recommendations to individual user preferences and behaviors.
3. Immersive Experiences with AR and the Metaverse
Augmented Reality (AR) is creating more interactive and immersive website experiences. Web developers are now incorporating AR as a learning tool, allowing users to virtually try products or visualize items in their own space. As the AR & VR market is projected to reach US$58.1 billion by 2028, its integration with the emerging Metaverse will open new frontiers for digital interaction.
4. Dark Mode for Enhanced User Experience
Dark mode has become a widespread trend that improves user comfort, especially on mobile devices. It reduces eye strain in low-light conditions and can help minimize battery drain. Known for its sleek and modern user experience, dark mode is solidifying its place as a staple in web design.
5. Minimalism & Clean Layouts
Prioritize simplicity to reduce cognitive load and make interfaces easier to navigate. By focusing only on essential elements, designers can guide users’ attention to key actions and information, improving task completion and overall usability. Clean layouts also enhance accessibility by avoiding clutter that can confuse users with cognitive or visual challenges. This approach not only makes digital products visually appealing but also increases user satisfaction, engagement, and retention across devices.
7 Common UI/UX Mistakes Beginners Make
Designing great user experiences is tricky, and beginners often stumble on similar issues. Here are the mistakes to watch out for:
-
Ignoring Mobile and Responsive Design
Many beginners design only for desktop screens, which can make apps or websites hard to use on phones and tablets. Always test your layouts on multiple devices and make sure everything adapts smoothly. -
Skipping User Research
Designing without understanding your users often leads to interfaces that look nice but don’t solve real problems. Spend time learning about your audience through surveys, interviews, or simple testing. -
Inconsistent Design Patterns
Using different styles for buttons, forms, or menus can confuse users. Stick to a consistent style for colors, typography, spacing, and interactions. -
Prioritizing Visuals Over Usability
A design can look beautiful, but if it’s hard to navigate, users will get frustrated. Make sure usability and clarity come before fancy visuals. -
Neglecting Accessibility
Ignoring accessibility excludes users with disabilities and limits your product’s reach. Follow basic accessibility standards, like proper color contrast, readable fonts, and keyboard navigation. -
Skipping User Testing
Assuming your design works without checking with real users often leads to overlooked issues. Test early, gather feedback, and make adjustments. -
Overcomplicating the Interface
Too many buttons, options, or animations can overwhelm users. Keep your interface simple and focused on the most important tasks.
Pro Tip: Focus on understanding your users, keeping designs consistent, and testing often. Small changes early on save time and create experiences that are easier and more enjoyable to use.
What is the Difference Between UI & UX?
UI (User Interface) and UX (User Experience) are related but distinct fields in the design of digital products. Here are some of the key differences between UI and UX:
- Focus: UI design is focused on the visual and interactive aspects of a product, including its layout, color scheme, typography, and the placement of buttons and other interface elements. UX design is focused on the overall experience of the user, including the product’s usability, accessibility, and emotional impact.
- Scope: UI design is a subset of UX design. While UI design is concerned with the look and feel of the product, UX design encompasses a broader range of factors, including user research, information architecture, and user testing.
- Skill set: UI designers need to have skills in visual design, graphic design, and front-end development. UX designers need to have skills in user research, information architecture, and interaction design.
- Tools: UI designers use tools such as Adobe Photoshop, Sketch, and Figma to create visual designs and interfaces. UX designers use tools such as user testing software, wireframing software, and prototyping tools to design and test user experiences.
- Output: The output of UI design is a set of visual designs and interface elements that are used to build the product. The output of UX design is a set of guidelines and best practices for creating a user-centered product.
Both fields are essential for creating products that are easy to use, efficient, and enjoyable for users.
| PROS AND CONS OF THE USER INTERFACE | |
| Pros | Cons |
| An aesthetically pleasing design can attract and retain users. | Focusing too much on aesthetics can sometimes compromise usability. |
| A clear and intuitive interface can make it easier for users to navigate and accomplish tasks. | Overuse of animation and effects can slow down the user experience. |
| Consistent design elements can increase user trust in the product. | Design trends can quickly become outdated, requiring constant updates. |
| Attention to detail can create a more polished and professional look and feel. | Design that is not consistent with the brand can be confusing for users. |
| User-centric design can create a more engaging and enjoyable experience. | A lack of user research and testing can result in a design that doesn’t meet user needs. |
| PROS AND CONS OF THE USER EXPERIENCE | |
| Pros | Cons |
| User-centric design can create a more satisfying experience for users. | It can be time-consuming and expensive to conduct thorough user research and testing. |
| A focus on usability and accessibility can make the product more inclusive. | Design decisions may be based on subjective opinions rather than data. |
| User testing can identify and fix issues before the product is launched. | Changes to the product based on user feedback may be difficult to implement. |
| Understanding user needs can result in a more efficient and streamlined product. | The user experience can be affected by factors outside of the designer’s control, such as network speed and device performance. |
| Attention to detail can create a more polished and professional product. | Too much focus on user needs can sometimes neglect business needs and goals. |
In summary, both UI and UX design have potential pros and cons, and the specific benefits and drawbacks will depend on the product, the users, and the design goals. If you are looking for expert assistance in your website development process, get in touch with Hurix Digital.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How do I choose between designing for mobile-first or desktop-first?
Mobile-first design is usually best if most users access your product via smartphones. Start by designing for smaller screens to prioritize essential features, then scale up for desktop. Desktop-first might make sense for enterprise tools used mainly on large screens. Consider your audience and analytics before deciding.
Q2:How can I make my UI more accessible without overcomplicating the design?
Focus on high contrast text, readable fonts, clear labels, and intuitive navigation. Use accessible color palettes and alt text for images. Avoid clutter while keeping interactive elements consistent, so users with visual, motor, or cognitive challenges can navigate easily.
Q3: How much user testing is enough for a beginner designer?
Even testing with 5–8 real users can reveal 80% of usability issues. Start small, observe how users interact with your prototype, collect feedback, iterate, and gradually scale testing as your project grows. Frequent short testing sessions are better than a single long session.
Q4: Can I learn UI and UX effectively without coding skills?
Yes. Beginners can start with design and prototyping tools like Figma, Adobe XD, and Sketch without coding. Understanding basic front-end concepts like responsive layouts helps, but coding is not required at the start. Learning to collaborate with developers is more important.
Q5: How do I balance aesthetics and usability in my designs?
A beautiful design is useless if it’s confusing to users. Prioritize functionality and clarity first, then enhance with colors, typography, and micro-interactions. Test designs regularly to ensure aesthetics don’t compromise usability.
Summarize with:

Associate Vice President – User Experience Design at Hurix Digital (EMEA), with 10+ years in UX and design leadership. She champions AI‑driven, inclusive, and strategy‑led UX across banking, fintech, EdTech, MedTech, and e‑commerce sectors.
 A Space for Thoughtful
A Space for Thoughtful 



