
Achieving IT Services Resilience at Negligible Cost: How to Build Disaster Recovery Site on Azure
Summary
This blog outlines Azure disaster recovery strategies, including DR types, setup for Azure/VMware VMs, failover processes, and DR drills, highlighting Azure’s key DR capabilities.
The seamless provision of IT services is particularly vital for the continuity and prosperity of a company in the present-day digital age. Since businesses are becoming increasingly dependent on technology, it is currently much more crucial to have the capability to get back to normal operation immediately, something that was unanticipated.
Increasing dependence by companies on technology and the ever-growing need to restore services after unscheduled outages are just a few reasons disaster recovery has become essential today. This is why organizations must have some sort of plan in place for dealing with unforeseen events without stopping operations completely.
Table of Contents:
- Why is There a Need for Disaster Recovery?
- Types of Disaster Recovery
- Set up Disaster Recovery for Azure VMs
- Failover Process
- Set Up Disaster Recovery for VMware VMs
- Failover and Failback
- Perform a Disaster Recovery Drill
- Conclusion
Why is There a Need for Disaster Recovery?
Disaster recovery is essential for many reasons in today’s technology-driven business environment. Some key points highlighting the need for disaster recovery include:
- Business Continuity: The processes in a business can come to a stop through some interruptions which may involve things like natural calamities or cyberattacks. This is where disaster recovery planning steps in ensuring such entities can maintain their essential functions without any extended periods of downtime.
- Data protection: One of an organization’s most important resources is data. Disaster recovery plans help prevent data loss or corruption and ensure that important information can be swiftly restored in times of need.
- Minimizing Financial Losses: The disturbance of operations, uncollected profits and higher money used for recovering from it can lead to huge financial losses as a result of a halt in its working which translates into lost time and information. Strategies designed to help an enterprise recover from disasters can help lessen these financial consequences.
- Operational Resilience: Including resilience in IT services helps businesses be more flexible and equipped to deal with unforeseen difficulties by preparing them for a variety of disruptions.
- Supporting Digital Transformation: As more companies use digital solutions, IT systems become more complicated and interdependent. Disaster recovery plans, which guarantee the resilience of the IT infrastructure, are essential to facilitating this transition.
Also Read: How to Set Up Azure Private Link for Enhanced Security and Data Protection?
Types of Disaster Recovery
1. Active – Active DR
Mirrored deployment stamps in two or more Azure regions, each configured to handle production workloads for the region or regions they serve and scalable to handle loads from other regions in case of a regional outage. An identical live infrastructure constantly mirrors the first site. The majority of organizations use this because it is quick and simple to obtain a lot of information after the causes have been identified. It is rarely identified as an option by small medium-sized businesses seeking disaster recovery. Most businesses do not choose it because it is expensive, and it requires a lot of bandwidth with fast response.
Advantages: High resiliency and low risk of full workload outage.
Disadvantage: Higher operating costs and management burden due to various factors, including the necessity of managing the synchronization of application state and data.
2. Active – Passive DR
One primary region and one or more secondary regions. The secondary region is deployed with the minimum possible compute and data sizing and runs without load. This region is known as a warm spare region. Upon failover, the compute and data resources are scaled to handle the load from the primary region. An active-passive DR solution creates an environment that is not intended to be live for IT production until the business declares a disaster. This creates large cost savings. A few of the application servers in use in an organization can be categorized as critical to its operations so the organization may opt to apply disaster recovery solutions on these only. In cases where several sites are involved the use of an active-passive disaster recovery solution would be preferable.
Advantage: Lower operating costs than the Active-Active DR design. The active-passive setup requires less hardware and is also more cost-effective. Passive nodes do not need to match the processing power of the active nodes which saves on costs. Because of its low cost, it is a desirable option for businesses looking for dependability without having to make large capital expenditures.
Disadvantage: Longer recovery time than the Active-Active DR design.
Set up Disaster Recovery for Azure VMs
Set up a virtual machine on Azure that can be replicated in another Azure region in case of disaster.
The following architecture provides a summary of the elements needed for disaster recovery for Azure virtual machines:
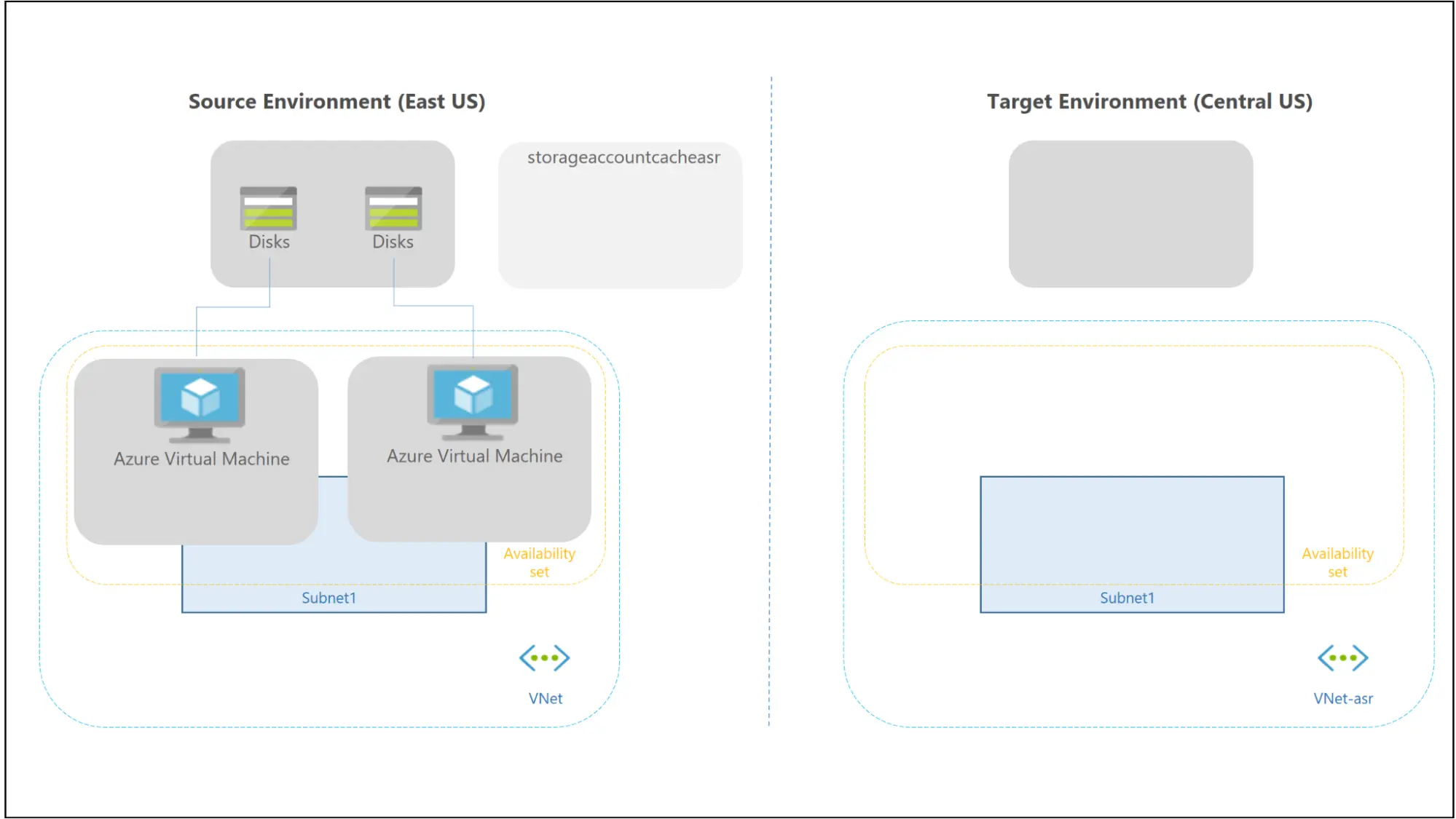
You can choose to have Site Recovery create target resources automatically when you enable replication for a virtual machine.
The following occurs when an Azure virtual machine (VM) has replication enabled.
- On the virtual machine, the Site Recovery Mobility service extension is installed immediately.
- The extension sets up Site Recovery for the virtual machine. Continuous replication begins for the VM.
- Disk writes are instantly moved to the source location’s cache storage account.
- Data in the cache is processed by Site Recovery before being sent to the intended storage account.
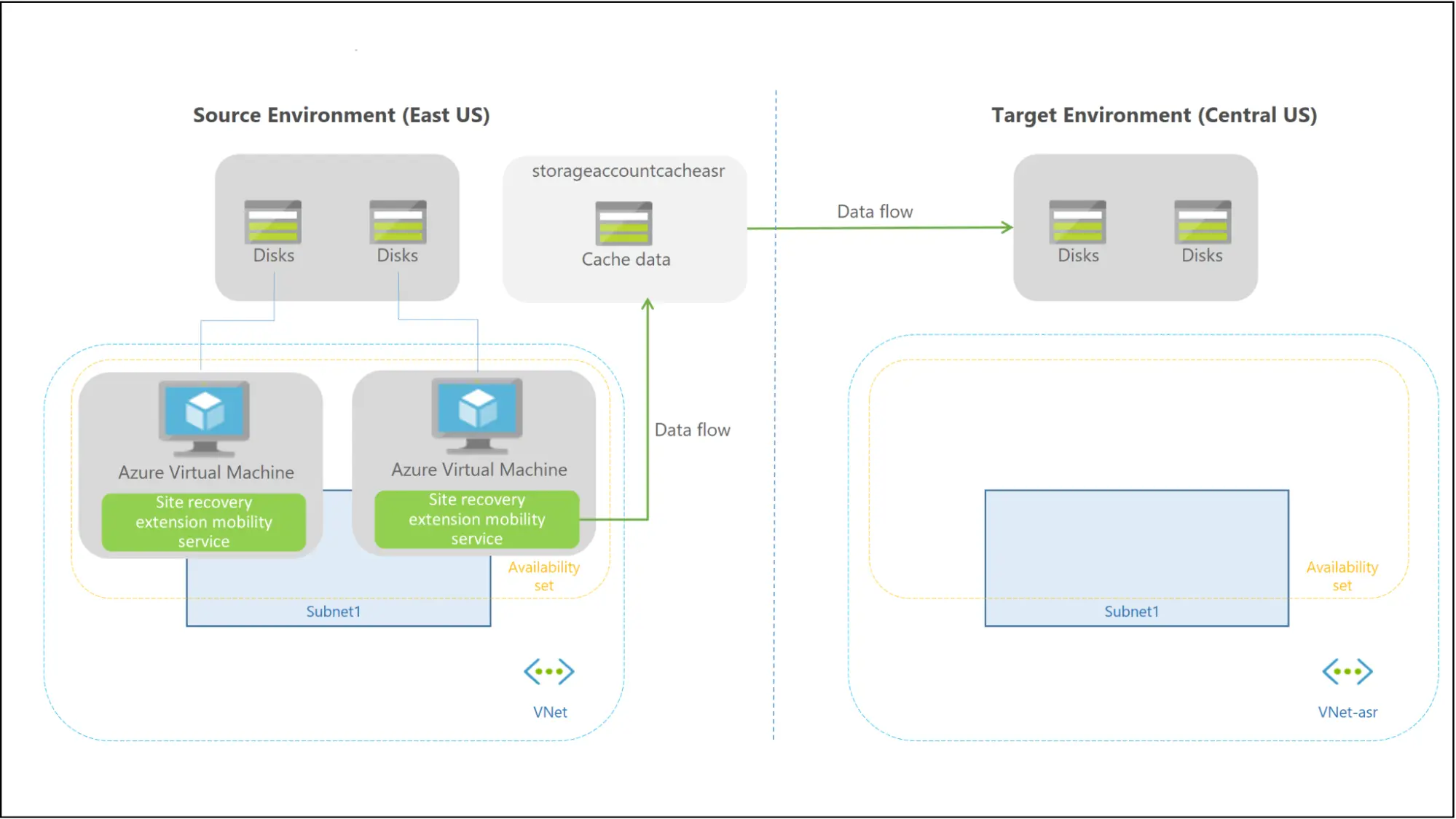
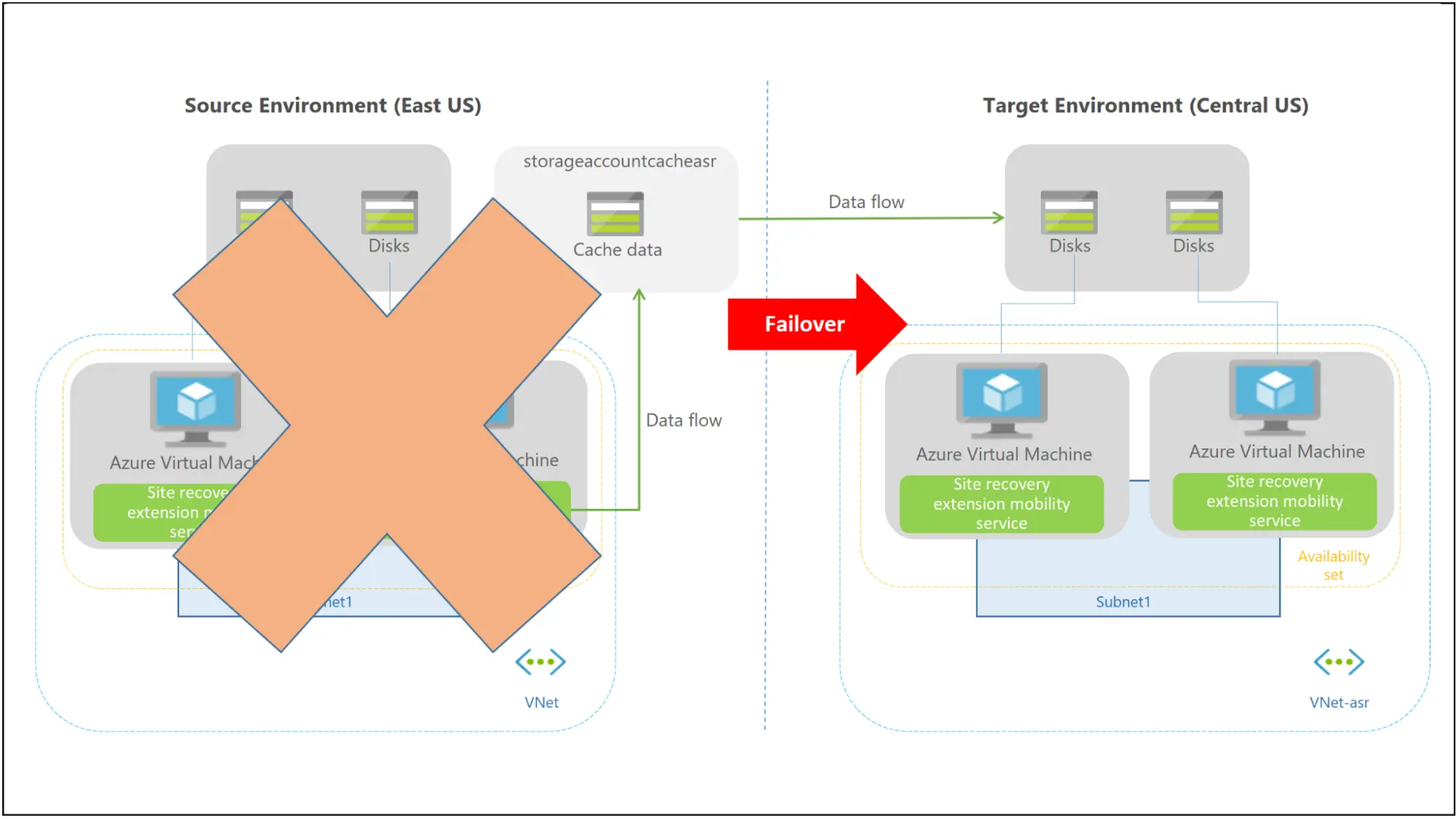
Failover Process
The virtual machines (VMs) are created in the target availability set, target virtual network, target subnet, and target resource group when you start a failover. You can use any recovery point in the event of a failover.
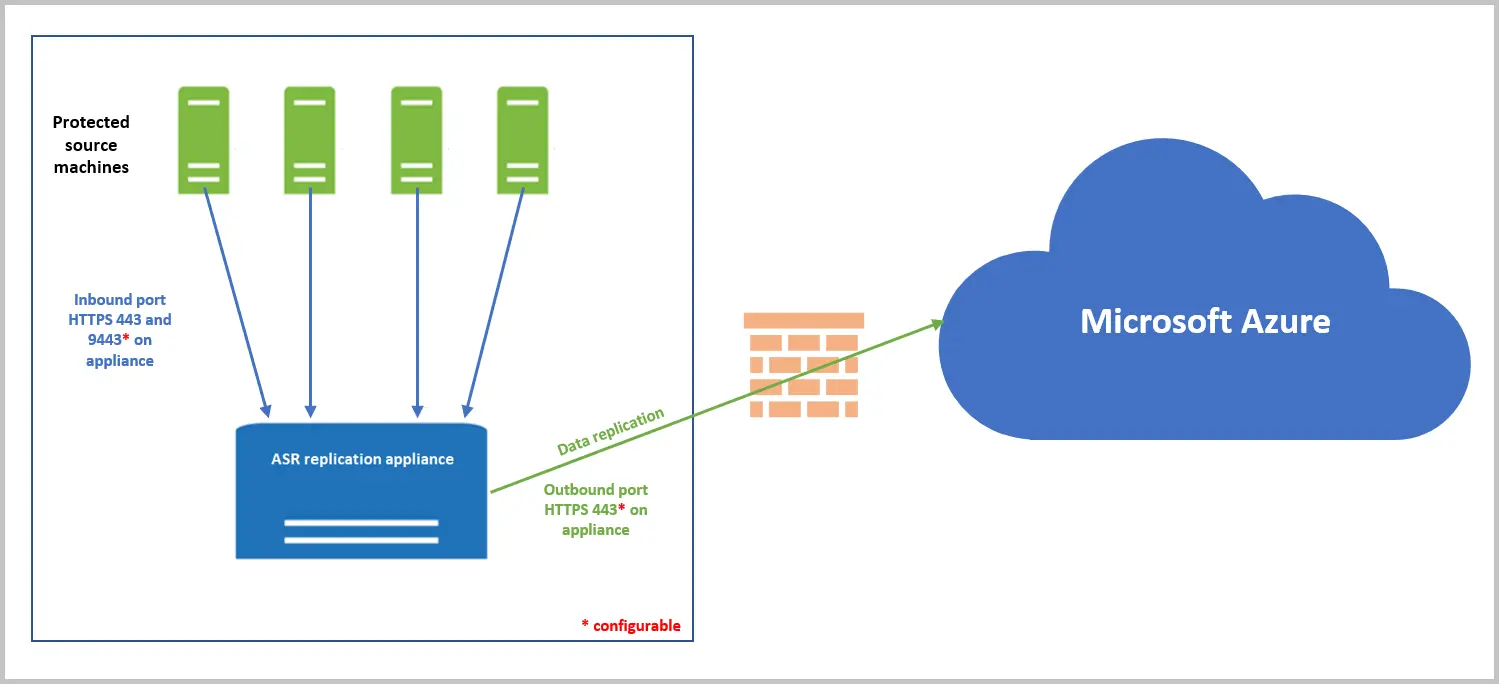
Set Up Disaster Recovery for VMware VMs
How to replicate on-premises VMware virtual machines to Azure? Here are the points to be noted before starting the replication:
- Each disk should be smaller than 4 TB when replicating to unmanaged disks and smaller than 32 TB when replicating to managed disks.
- The operating system disk should be a basic disk, not a dynamic disk.
- For generation 2 UEFI-enabled virtual machines, the operating system family should be Windows, and the boot disk should be smaller than 300 GB.
The components utilized for VMware virtual machines’ disaster recovery to Azure are shown in high detail in the architecture and image that follow.

Initial replication to Azure storage using the designated replication policy starts when you enable replication for a virtual machine.
The replication data logs initially end up in an Azure cache storage account. After these logs are examined, the information is saved on an Azure Managed Disk, also known as “asrseeddisk”. This disk is where the recovery points are produced.
Failover and Failback
One can do failover and failback as needed once replication is configured and a disaster recovery drill (test failover) is conducted to ensure everything is operating as planned.
Perform a Disaster Recovery Drill
Here’s a Disaster Recovery Testing Plan:
- Test Failover: Used to execute a drill that validates your Disaster recovery strategy, without any data loss or downtime.
Recommendation to perform every month for critical workloads.
- Planned Failover: Used when there are arranged outages because VM sources are shut down. Failover only kicks in when the latest data has been synced.
Recommendation to perform quarterly.
- Failover: is typically activated in the event of an unforeseen disruption, or when the main site is inaccessible. Optionally turn off the virtual machine and synchronize its latest changes before activating failover.
- Check to ensure that every critical system, application, and data is working well in the disaster recovery environment.
- Restore the Production environment in Production from the DR environment and then perform a failback test.
- Report findings of DR test results to the stakeholders and management.
Check out EXCLUSIVE: Hurix Digital Secured 99.9% Uptime for a $800M Retail Giant Using Azure Disaster-Recovery Solution
Conclusion
Azure Catastrophe Disaster Recovery Service gives you a plug-and-play toolkit to prepare your organization for tomorrow and react at the same time. Diverse scalability, configurable methods, and sophisticated features are capabilities that make Azure a game changer in the Disaster Recovery Sector. In hindsight, Azure has a strong infrastructure, Cost management tools, regular testing frameworks, and the latest features for keeping your company safe from current or looming dangers.
Visit Hurix Digital’s Cloud Services to get a smooth cloud adoption journey.

Vice President and Strategic Business Unit Head – Cloud Services
A top technology management voice on LinkedIn with 20 Years of experience in Information Technology, Cloud Services, Digital Transformation, Application Modernisation, Managed Services, IT Security Engineering and Operations Management. An avid technology Leader, Leadership Speaker, Author & Coach.







